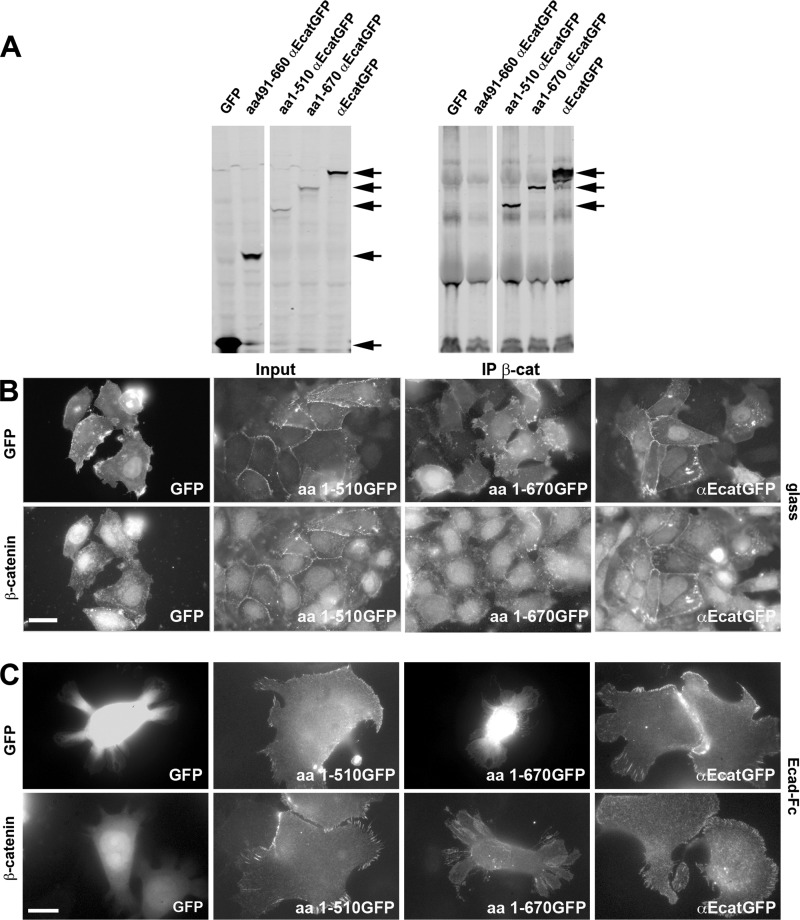
FIGURE 3.
Characterization of αE-catenin mutants and their effect on αE-catenin-depleted cell-cell junction formation, cell spreading, and the formation of cadherin adhesion on Ecad-Fc-coated surfaces. A, characterization of αE-catenin mutants for their capacity to bind to β-catenin. Cell lysates of transfected DLD-1-R2/7 cells expressing GFP alone, the αE-catenin mutants (aa491–660 αEcatGFP, aa1–510 αEcatGFP, and aa1–670 αEcatGFP), or αEcatGFP were immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-β-catenin antibody and analyzed by Western blot with an anti-GFP antibody (right). The arrows indicate the position of the band corresponding to GFP-tagged αE-catenin and the mutants that co-precipitate with β-catenin. Note that GFP alone and the αE-catenin mutant corresponding to the modulation domain (aa491–660 αEcatGFP) do not co-precipitate with β-catenin. The corresponding cell lysate inputs are presented in the left panel. B, localization of GFP (top panels) and β-catenin (bottom panels) in DLD-1-R2/7 cells transiently transfected with plasmids encoding GFP alone, αEcatGFP, and aa1–510 or aa1–670 αEcatGFP mutant. GFP-transfected and non-transfected cells did not form cell-cell contacts. However, cells transfected with a αEcatGFP construct readily formed cell contacts and recruited β-catenin at their boundaries. Cells transfected with the aa1–510 αEcatGFP mutant were indistinguishable from αEcatGFP-transfected cells. Surprisingly, the slightly longer mutant (aa1–670) restored neither cell contact formation nor the recruitment of β-catenin. C, localization of GFP (top panels) and β-catenin (bottom panels) in transiently transfected cells to express αEcatGFP, aa1–510 αEcatGFP, or aa1–670 αEcatGFP mutant and GFP after spreading for 16 h on Ecad-Fc-coated surfaces. Scale bar, 10 μm.