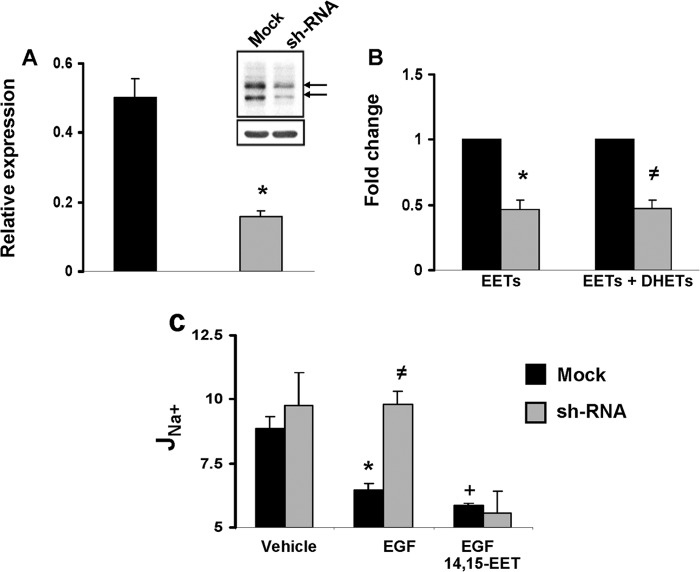
FIGURE 4.
CYP2C44 knockdown reduces epoxygenase expression and blunts the effects of EGF on sodium transport. A, quantitative real time PCR analysis of mRNAs present in cells expressing non-coding (mock) (black bars) or CYP2C44-coding silencing RNAs (shRNA) (gray bars) using CYP2C44-selective primers (23). Values, normalized to β-actin mRNA levels, are averages ± S.E. (error bars) calculated from three different cell samples, each analyzed in triplicates. Difference from mock cells is indicated as follows: *, p < 0.004. Inset, Western blots of lysates from mock and shRNA cells probed with anti-CYP2C44 antibodies (upper panel) and normalized to the levels of anti-β-actin immunoreactive protein (lower panel). The arrows indicate approximate mobilities for 56- and 65-kDa proteins. B, the sum of EETs and dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids (DHETs) present in mock and shRNA cells was extracted and quantified using ultrahigh pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric techniques as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Values are -fold change averages calculated from three different experiments. Differences from mock controls are indicated as follows: *, p < 0.02; ≠, p < 0.04. C, amiloride-sensitive JNa+ responses for mock (black bars) and shRNA cells (gray bars) exposed to vehicle or EGF (10 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of 14,15-EET (5 μm). Values (in pmol/h/cm2) are averages ± S.E. (error bars) calculated from five cell samples. Differences are indicates as follows: from vehicle-treated mock cells: *, p < 0.004; +, p < 0.001; from EGF-treated mock cells: ≠, p < 0.04. The differences between vehicle- and EGF-treated shRNA cells, EGF- and EGF plus 14,15-EET- treated mock cells, and EGF plus 14,15-EET-treated mock and shRNA cells were not significant (p > 0.05).