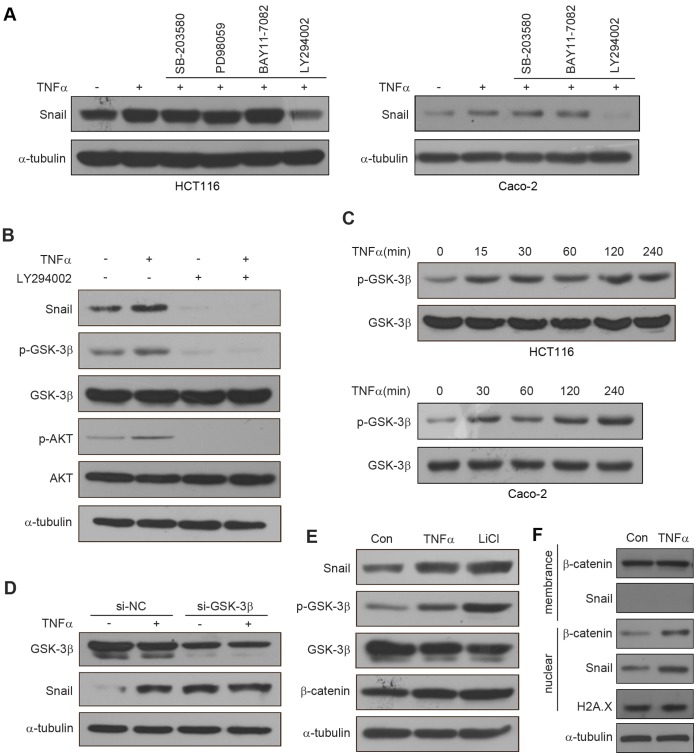
Figure 5. TNFα stabilizes Snail through AKT/GSK3β.
pathway. (A) HCT116 cells were pretreated with SB-203580 (20 µM), PD98059 (20 µM), BAY11-7082(10 µM), LY294002 (20 µM) for 1 h respectively followed by stimulation with TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 6 h. The expression of Snail was examined by western blotting. Caco-2 cells were pretreated with SB-203580 (20 µM), BAY11-7082(10 µM), LY294002 (20 µM) for 1 h respectively followed by stimulation with TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 6 h. The expression of Snail was examined by western blotting. (B) HCT116 cells were pretreated with or without LY294002 (20 µM) for 1 h, followed by stimulation with or without TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 6 h. The expression of Snail and the activation of AKT and GSK-3β were examined by western blotting. (C) HCT116 and Caco-2 cells were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) for the times indicated. The expression of pGSK-3β and GSK-3β were examined by western blotting. (D) Control and GSK-3β si-RNA were expressed in HCT116 cells for 42 h, followed treated with or without TNFα (20 ng/ml) for additional 6 h. The expression of Snail and GSK-3β were examined by western blotting. (E) HCT116 cells were treated with TNFα (20 ng/ml) or LiCl (40 mM) for 6 h. The expression of Snail, pGSK-3β, GSK-3β, and β-catenin were analyzed by western blotting. (F) After treated HCT116 cells with or without TNFα (20 ng/ml) for 6 h, Snail and β-catenin located at membrane and nuclear were isolated respectively and then analyzed by western blotting.