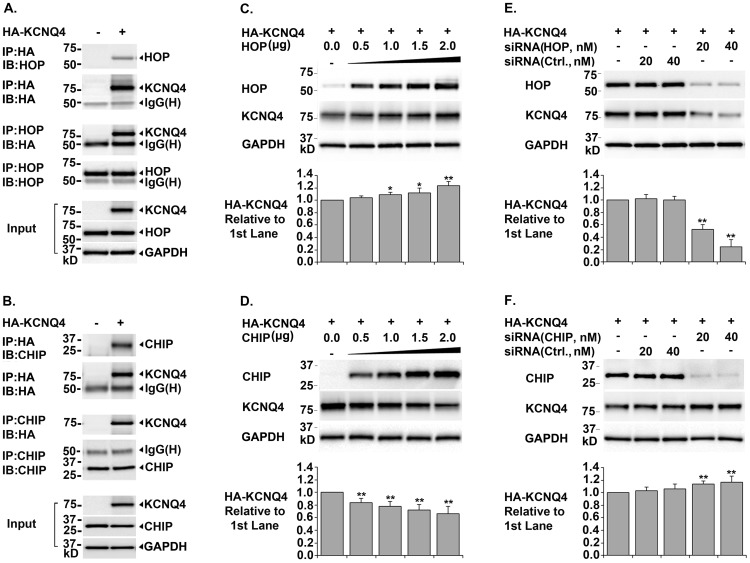
Figure 3. Roles of Cochaperones HOP and CHIP in KCNQ4 Biosynthesis.
A. & B. Co-immunoprecipitation of KCNQ4 channels with cochaperones HOP and CHIP HEK293T cells were transfected with 0.4 µg of pCMV6-XL5-HA-KCNQ4 (+) or pCMV6-XL5 (-) and cultured for 24 hrs. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was done using antibodies either against the HA tag in KCNQ4 channels or a cochaperone (HOP or CHIP). The precipitate was analyzed by Western blot (IB) using the indicated antibodies. Cell lysates were tested in parallel for HA-KCNQ4, cochaperones, and GAPDH as input controls. Association of HOP and CHIP with KCNQ4 channels were confirmed by co-precipitation of these proteins. C. & D. Effects of over-expression of HOP or CHIP on total KCNQ4 level HEK293T cells were transfected with 0.4 ug of pCMV6-XL5-HA-KCNQ4 (+) and different amount of cochaperone cDNA as indicated. 24 hrs post transfection, the cells were lysed in NP40 lysis buffer and the cell lysates were tested for total KCNQ4 proteins by Western blot. Over-expression of cochaperone HOP led to a significant increase, whereas over-expression of CHIP resulted in a marked decrease in total KCNQ4 level. E. & F. Effects of siRNA knockdown of HOP or CHIP on total KCNQ4 level HEK293T cells were transfected with 0.4 µg of pCMV6-XL5-HA-KCNQ4 (+) and various amount of siRNA as indicated. The transfected cells were cultured for 48 hrs and the cell lysates were tested for KCNQ4 proteins. Knockdown of cochaperone HOP led to a marked decrease, while knockdown of CHIP resulted in a significant increase in total KCNQ4 level. Each data point in the bar graphs represents the mean ±SD of three experiments (* p≤0.05, ** p≤0.01).