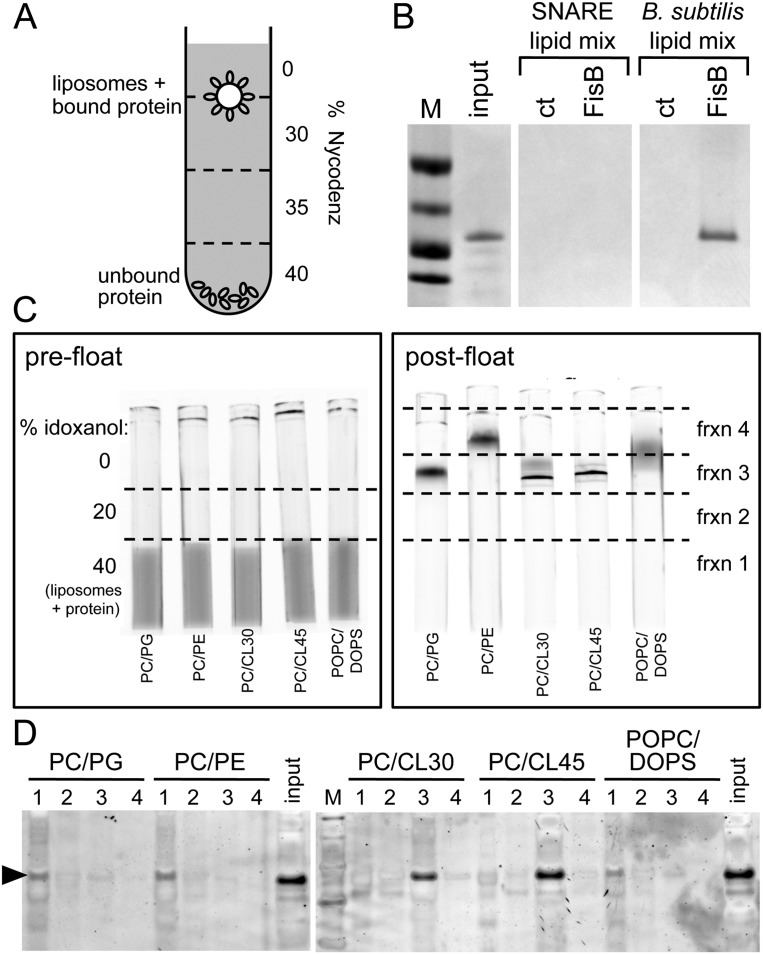
Figure 5.
The extracellular domain of FisB binds CL in vitro. (A) Schematic representation of the coflotation assay. Protein-free liposomes were incubated with the soluble extracellular domain of FisB (ovals) for 2 h at room temperature. Liposomes and bound protein were separated from unbound protein using a four-step Nycodenz gradient. (B) The interface between the 0% and 30% step was collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie blue. FisB bound to liposomes composed of a mixture of B. subtilis lipids (PG/PE/CL/PC) but not to liposomes used in SNARE fusion assays (POPC/DOPS). Input protein (20% of what was used in the binding assay) was loaded for comparison. Fractions from a step gradient lacking FisB are shown (ct). Molecular weight standards (50, 37, 25, and 20 kDa) (M) are indicated. (C,D) Coflotation assay in which the lipid composition of the liposomes was varied: PC/PG (70 mol/30 mol), PC/PE (70 mol/30 mol), PC/CL30 (70 mol/30 mol), PC/CL45 (55 mol/45 mol), and POPC/DOPS (85 mol/15 mol). (C) All liposomes contained a small percentage of NBD-PE as a fluorescent marker. Visualization of liposomes by fluorescence before (prefloat) and after (post-float) separation using a three-step idoxanol gradient (see the Materials and Methods). (D) Four fractions were collected as indicated in the post-float box and analyzed by SDS-PAGE stained with SYPRO Orange. FisB bound efficiently to liposomes containing CL but not to liposomes without CL.