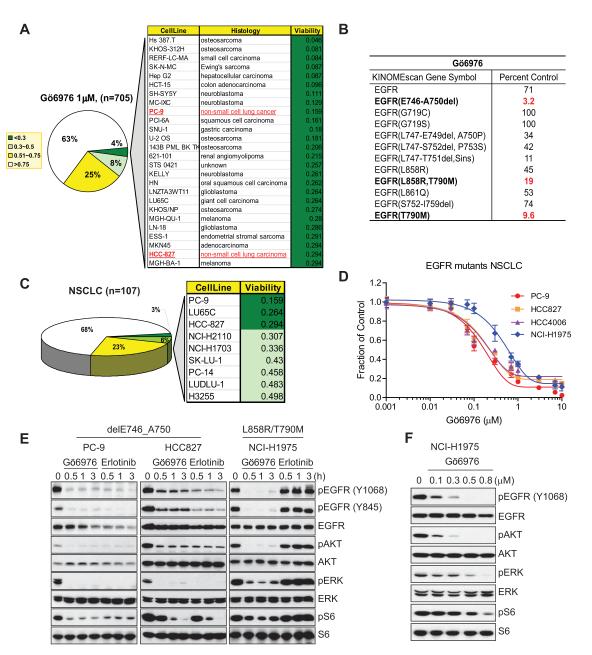
Figure 1.
Gö6976, a classical PKC inhibitor, inhibits the viability of EGFR mutant NSCLC cell lines. A, Pie chart representing the Gö6976 sensitivity distribution (1 μM) across 705 tested tumor cell lines treated for 72 hr. The legend indicates the sensitivity as measured by the fraction of viable cells relative to untreated controls. Details for 4% of the most sensitive cell lines are shown in the chart and the cell lines are listed in order of decreasing sensitivity. B, Ambit kinome screening results for Gö6976. Kinome profiling was performed using a panel of 442 human kinases on Gö6976 (500 nM). The potential targets are indicated in bold and corresponding inhibitory scores (the percent of DMSO control) are in red. C, Pie chart representation of the Gö6976 sensitivity of 107 tested NSCLC lines. Among the 10 NSCLC lines most sensitive to Gö6976, 3 cell lines, PC-9, HCC-827, and PC-14, harbor activating EGFR mutants. D, Confirmation of Gö6976 efficacy in EGFR mutant-driven NSCLCs. PC-9, HCC827, HCC4006, or NCI-H1975 cells were treated with Gö6976 at the indicated concentration for 72 hr. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. E, Comparison of potency between Gö6976 and erlotinib on EGFR signaling in EGFR mutant-driven NSCLCs. del E746_A750-driven PC-9 or HCC827 cells or L858R/T790M-driven NCI-H1975 cells were treated with either 1 μM Gö6976 or erlotinib for the indicated times followed by immunoblotting with antibodies to detect effects on EGFR signaling. Erlotinib did not affect EGFR signaling in NCI-H1975 cells. F, Potency of Gö6976 in NCI-H1975 cells. Gö6976 treatment in NCI-H1975 at various concentrations for 3 hr. IC50 concentration for suppression of pEGFR is ~100 nM.