Figure 8.
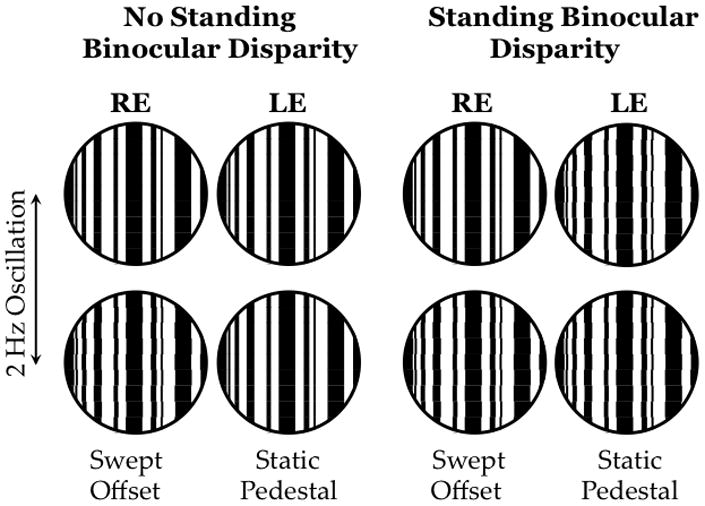
Schematic of the stimuli used to assess fusional suppression.(Fu et al., 2006) Stimuli were dichoptic (anaglyphic) multi-bar vernier targets. When there was no standing binocular disparity present (left), 5 static segments interspersed with 4 oscillating segments that aligned and misaligned at 2 Hz. The magnitude of the misalignment offset was swept in 7 steps from 10 to 1 min over each 7 sec trial while the other eye viewed a static multi-bar target with 0 min standing binocular disparity. The VEP was elicited by the making and breaking of co-linearity in the eye that viewed the vernier offsets. The standing disparity condition was similar except that the other eye viewed static multi-bar target with 5 min standing disparity. As in the other condition, the VEP was elicited by the making and breaking of co-linearity in the eye that viewed the vernier offsets; any difference in VEP amplitude between the two conditions is due to a suppressive effect of the static binocular disparity on the monocular vernier position response.
