Fig. 3.
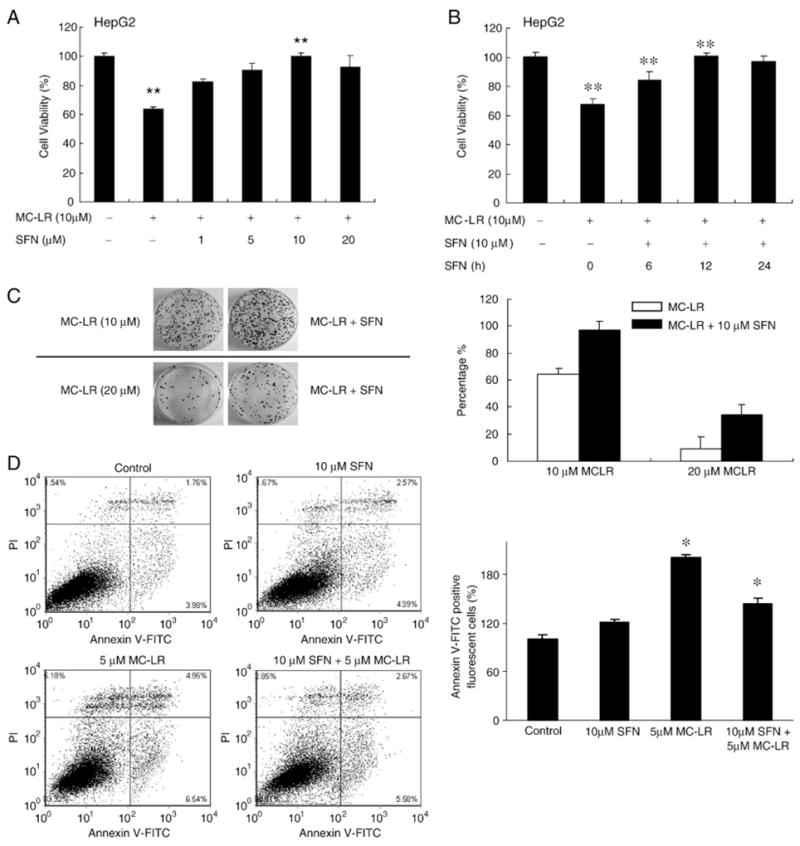
SFN protects HepG2 cells from MC-LR-induced cytotoxicity. (A) HepG2 cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of SFN for 12 h, and then treated with MC-LR for 24 h. (B) is the assay results of different pretreatment times. 0 h means cells were treated with SFN and MC-LR at the same time. The cell viability was determined by MTS assay. Each value represents the mean±S.D. of three determinations. **, p<0.01. (C) Colony formation assay confirms cytoprotection by SFN. Left, colony formation images in HepG2 clones after 2 weeks. Cells were pretreated with or without 10 μM SFN for 12 h and then treated with MC-LR for another 24 h, as indicated in materials and methods. Right, percentage of viable HepG2 cells after 2 weeks with MC-LR treatment for 24 h in the presence or absence of SFN. Error bars indicate the S.D. (n=3). (D) SFN pretreatment inhibits MC-LR-induced apoptotic cell death. Cell death in HepG2 cells with or without pretreatment with 10 μM SFN for 12 h and then treated with MC-LR for another 24 h. Apoptotic cell death was detected using Annexin V-FITC staining and flow cytometry. The bar graph was the proportion of early apoptotic cells plus late apoptotic cells comparing with control; the mean±SD was calculated from experiments run in triplicate (right).
