Figure 2. Model of the CB ‘quadripartite synapse’.
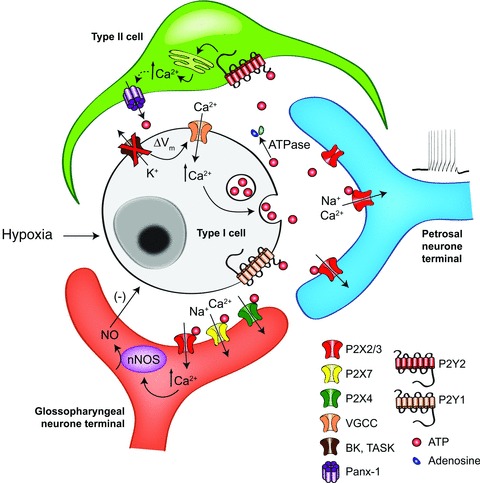
Release of ATP from type I cells during hypoxia excites sensory terminals; note role of type II cells in amplifying the ATP signal via P2Y2 receptors and the opening of pannexin-1 channels. Negative feedback pathways include inhibitory action of NO released from efferent nerves and ATP-mediated paracrine inhibition of type I cells. Note that the roles of other well-described CB neurotransmitters and neuromodulators, including ACh, dopamine and adenosine, as well as their respective signalling pathways (see Shirahata et al. 2007; Iturriaga et al. 2009; Nurse, 2010; Conde et al. 2012; Nurse & Piskuric, 2012), have been omitted here for clarity.
