Figure 1. Junctophilin-1 (JP1) and junctophilin-2 (JP2) undergo Ca2+-dependent proteolysis by endogenous proteases.
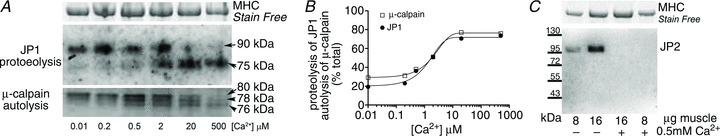
A, Western blot of human skeletal muscle cryosections following exposure to various set levels of [Ca2+] for 60 min at room temperature. Whole muscle was separated on 10% Stain Free gels and probed using a mid-region JP1 antibody, which detects full-length 90 kDa JP1 and proteolysed 75 kDa JP1. Myosin heavy chain (MHC) bands in Stain Free gel were used as a loading control (top panel). A separate gel was run to detect μ-calpain in same homogenate samples (bottom panel). Full-length μ-calpain is detected at 80 kDa, and autolyses to 78 and 76 kDa forms, indicating that it has been activated. B, the percentage proteolysis (JP1) or autolysis (μ-calpain) following exposure to the indicated [Ca2+]; data are mean values from two repeats on separate gels. C, Western blot of JP2 in rat extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle homogenates treated without or with 0.5 mm Ca2+ for 60 min at RT, separated on a 4–15% Stain Free gel.
