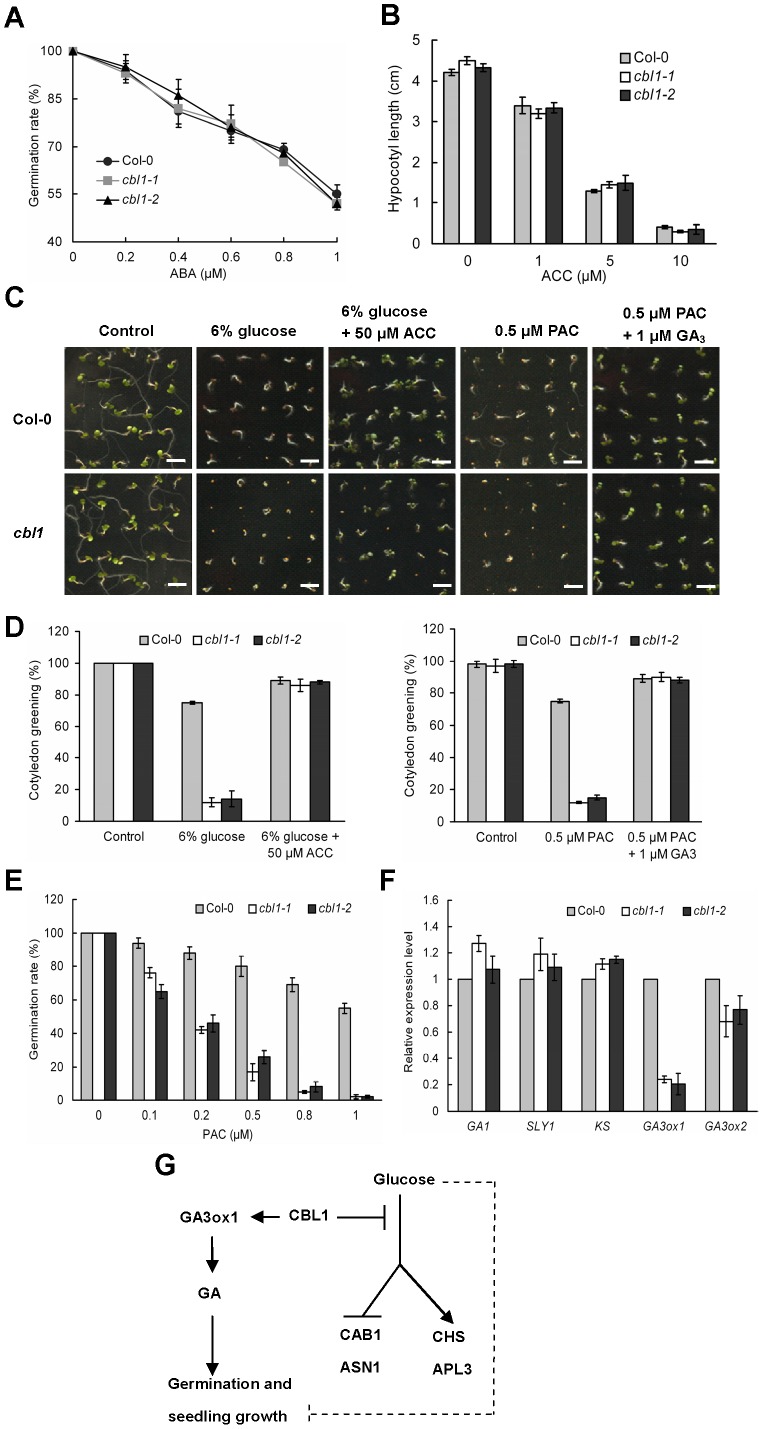
Figure 3. Phytohormones responses in cbl1 mutant plants.
(A) Germination rates of Col-0 and mutant seeds after 5 d of incubation at 22 °C on ½ MS medium containing different concentrations of ABA. Results are presented as average values ± SE from three experiments. (B) Effect of ACC on hypocotyls elongation in Col-0 and mutant. Hypocotyl lengths were measured 5 d after stratification of seedlings grown in the dark in the presence of different concentrations of ACC. (C) Representative images of Col-0 and mutant grown in conditions indicated above the images for 7 days. Bars = 5 mm. (D) Comparison of percentage green cotyledons of Col-0 and mutant seedlings grown in control conditions or in the presence of 6% glucose supplemented or not with 50 µM ACC or in the presence of 0.5 µM PAC supplemented or not with 1 µM GA3. Data are averages of 60 plants ± SD. (E) Germination of Col-0 and mutant grown in medium with different concentrations of PAC. Each point represents averages of 80 seeds ± SD. (F) Relative expressions of GA biosynthetic and signaling genes in two-week-old seedlings of Col-0 and mutant grown on MS medium. G1D1, GA INSENSITIVE DWARF1A; SLY1, SLEEP1; KS, ent-kaurene synthase; GA3ox: GA3-oxidase. (G) A model to explain CBL1 function in glucose- and GA-responsive gene expression. CBL1 might positively modulate GA response via regulation of GA3ox1, and affects both glucose-induced and glucose-repressed gene expression.