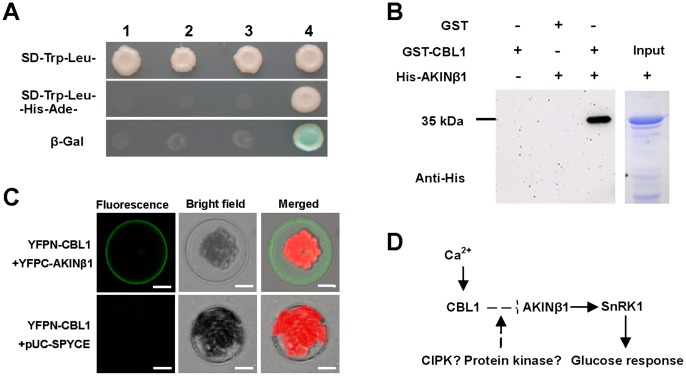
Figure 4. Interaction between CBL1 and AKINβ1.
(A) Yeast two-hybrid interactions. Vectors were co-introduced into yeast AH109 strain in different combinations: 1, pGADT7 and pGBKT7; 2, pGADT7-AKINβ1 and pGBKT7; 3, pGADT7 and pGBKT7-CBL1; 4, pGADT7-AKINβ1 and pGBKT7-CBL1. Transformants were placed on selection medium and grown for 4 d before the β-galactosidase (β-Gal) assay. (B) In vitro GST pull-down assay. GST-CBL1 and His-AKINβ1 were expressed in E. coli and used for analysis. The presence or absence of each protein in the reaction mixture is shown as+or -, respectively. The right row shows a Coomassie Brilliant Blue-stained SDS-PAGE gel indicating captured proteins used as controls. Experiments were performed 3 times and a representative result was shown. (C) In vivo BiFC assay. The plasmids YFPN-CBL1 and YFPC-AKINβ1 were co-transformed into Arabidopsis protoplasts. The expression of CBL1 alone (YFPN-CBL1+ pUC-SPYCE) was used as control. Photographs were taken with a confocal laser-scanning microscope (Leika TCS-NT). Bars = 10 µm. (D) A proposed model to illustrate biological relevance of the interaction between CBL1 and AKINβ1. In the presence of calcium, CBL1 together with certain CBL-interacting protein kinases (not only CIPK) forms a complex to modify AKINβ1, thus affecting the activity of SnRK1. Positive interaction is noted by an arrow and bars indicate repression.