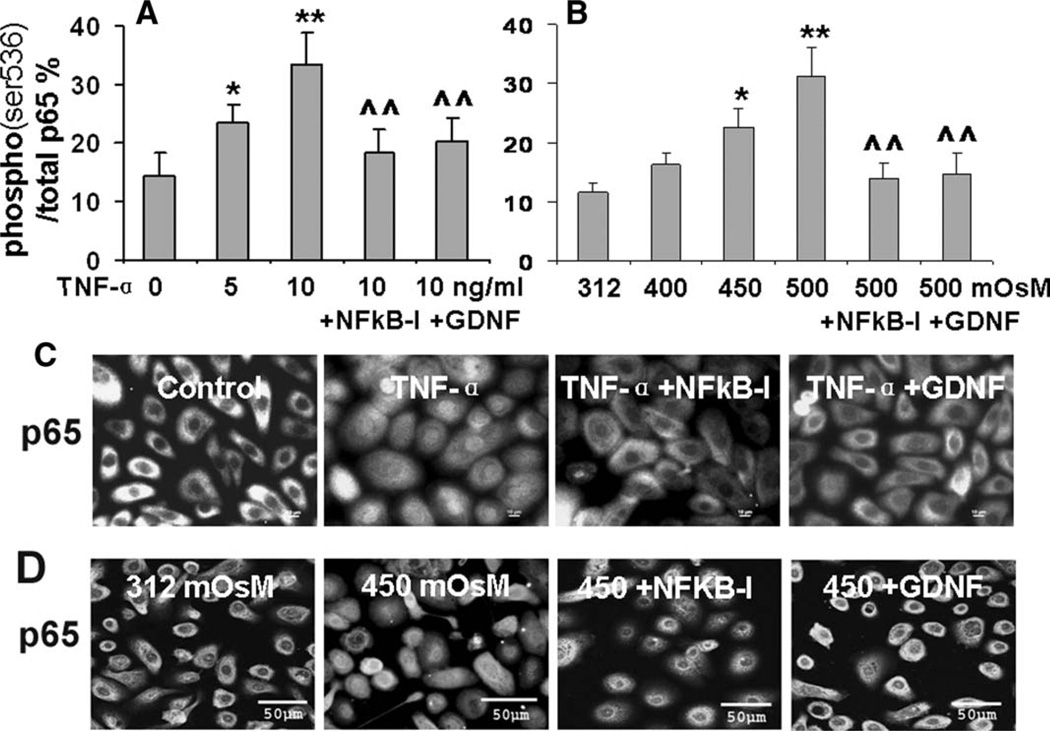
Figure 5.
Suppressive effect of GDNF on NF-κB activation in human limbal epithelial cells (HLECs) stressed with TNF-α or hyperosmotic media. The HLECs were preincubated with 5 µM quinazoline NF-κB-I or 10 ng/ml GDNF for 1 hour before treatment with TNF-α (5–10 ng/ml; [A], [C]) or hyperosmotic media (400–500 mOsM; [B], [D]). The cells in 96-well plates treated for 30 minutes were used for cell-based enzymelinked immunosorbent assay quantification of p65 (ser536) phosphorylation (% Phospho-/total p65; [A], [B]). Results shown are mean ± SD of three independent experiments, *, p < .05; **, p < .01, compared with controls; ^, p < .05; ^^, p < .01, compared with the stimulated levels, by ANOVA test. The cells seeded in eight-chamber slides were fixed with methanol for immunofluorescent staining with rabbit anti-human p65 antibody and Alexa-Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibodies ([C], [D]). The images were representative of those observed in the three independent experiments. Abbreviations: GDNF, glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor; NF-κB-I, NF-κB inhibitor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.