Figure 5. The temporal characteristics of auditory-language-related gamma-augmentation in the left hemisphere.
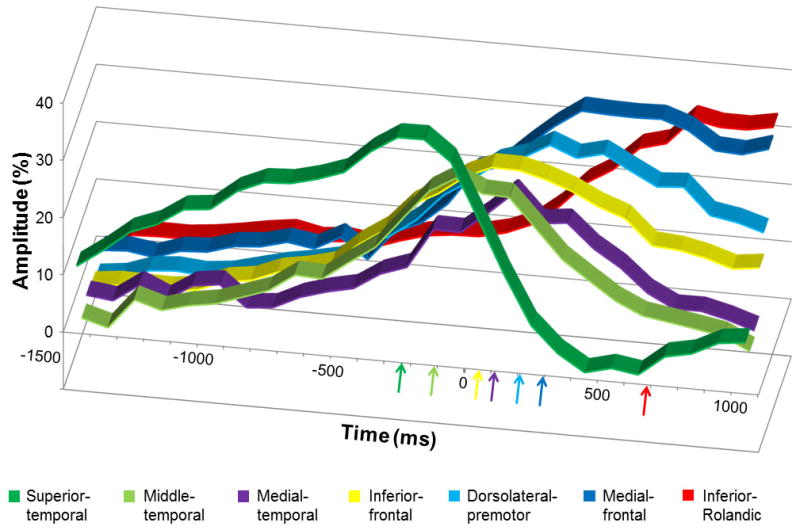
The X-axis shows the time in ms, and +/− 0 ms reflects the offset of question. The Y-axis shows the average percent change of gamma-amplitudes at 80–100 Hz compared to those during the reference period 3000 to 2600 msec prior to the offset of question. Gamma-augmentation reached the peak sequentially in the superior-temporal (−230 msec prior to the stimulus offset), middle-temporal (−110 msec), inferior-frontal (50 msec), medial-temporal (110 msec), dorsolateral-premotor (210 msec), medial-frontal (290 msec), and inferior-Rolandic regions (680 msec). The presented data are derived from patients with essential language function assumed to remain in the left hemisphere.
