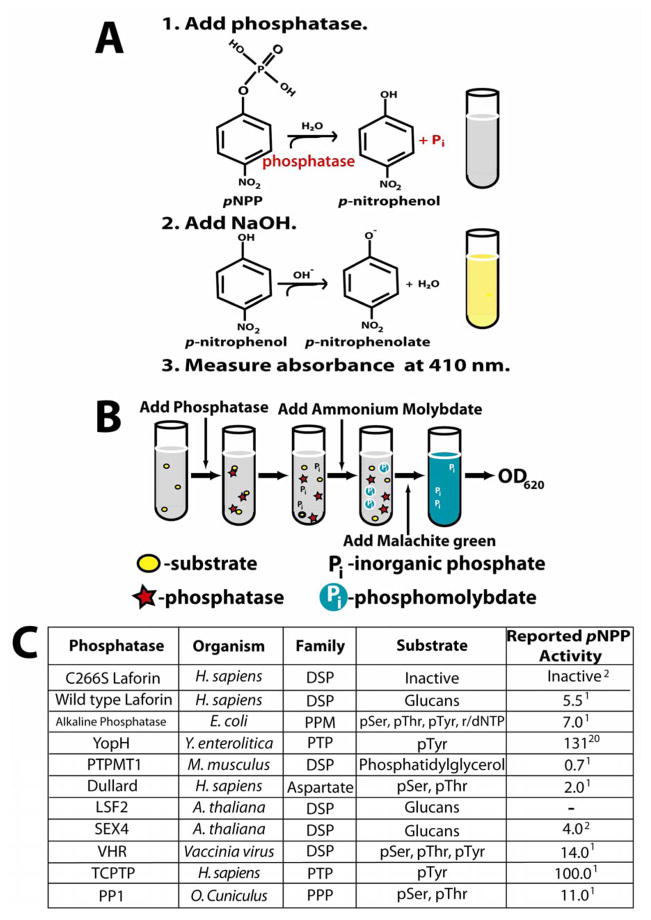
Figure 1. Experimental design of assays and phosphatases chosen for study.
A. The pNPP assay. Hydrolysis of the aryl phosphate moiety from the small molecule para-nitrophenylphosphate (pNPP) converts this colorless substrate into para-nitrophenol, which forms the bright yellow phenolate ion under alkaline conditions (pKa of 7.2). The presence of the soluble phenolate ion can be observed by reading the absorbance at 410 nm. When performing this colorimetric assay under saturation conditions of substrate as we have done, it is possible to calculate the rate of dephosphorylation as well as kinetic constants such as kcat and KM [10,12]. While pNPP is an artificial substrate, the small size of this molecule restricts interaction to a low number of residues, allowing resolution of active site conformation changes due to mutation [12]. Phosphatase assays involving these substrates can be performed in a continuous or discontinuous fashion. Continuous enzyme assays, allowing hydrolysis products to be quantified without disturbing the reaction, are superior to discontinuous assays in the efficiency of determining kinetic constants [10]. However, for the purpose of this work, discontinuous assay under saturated conditions was sufficient (10 times the Km) [12], providing the initial (linear) rate of the reaction for phosphatase activity comparison.
B. The malachite green assay utilizing amylopectin as a substrate. As phosphate monoesters in amylopectin are hydrolyzed, the free phosphate forms a complex with the ammonium molybdate in the malachite green reagent. At low pH, the basic malachite green dye forms a complex with phosphomolybdate and shifts to its absorption maximum. This complex is stabilized for up to 48 hours by detergents such as Tween 20 [27], allowing for easy colorimetric detection that is linear with as little as 50 to 1000 pmol of Pi following measurement of the absorbance at 620 nm [15]. While it is not possible to calculate enzyme kinetics using the heterogeneous amylopectin polymer, use of amylopectin as a substrate allows for the detection of glucan phosphatase activity. For both the malachite green and pNPP assay, dithiothreitol (DTT) was used as the reducing agent to maintain enzyme activity as malachite green is sensitive to 2-mercaptoethanol [14].
C. List of phosphatases used in the pNPP and malachite green assays. Phosphatases across families and within families were chosen to obtain a representative and diverse collection of enzymes for study. Included in the list is the family and organism of origin and the known substrates and reported specific activity against pNPP (μmol/min/mg) for each enzyme.