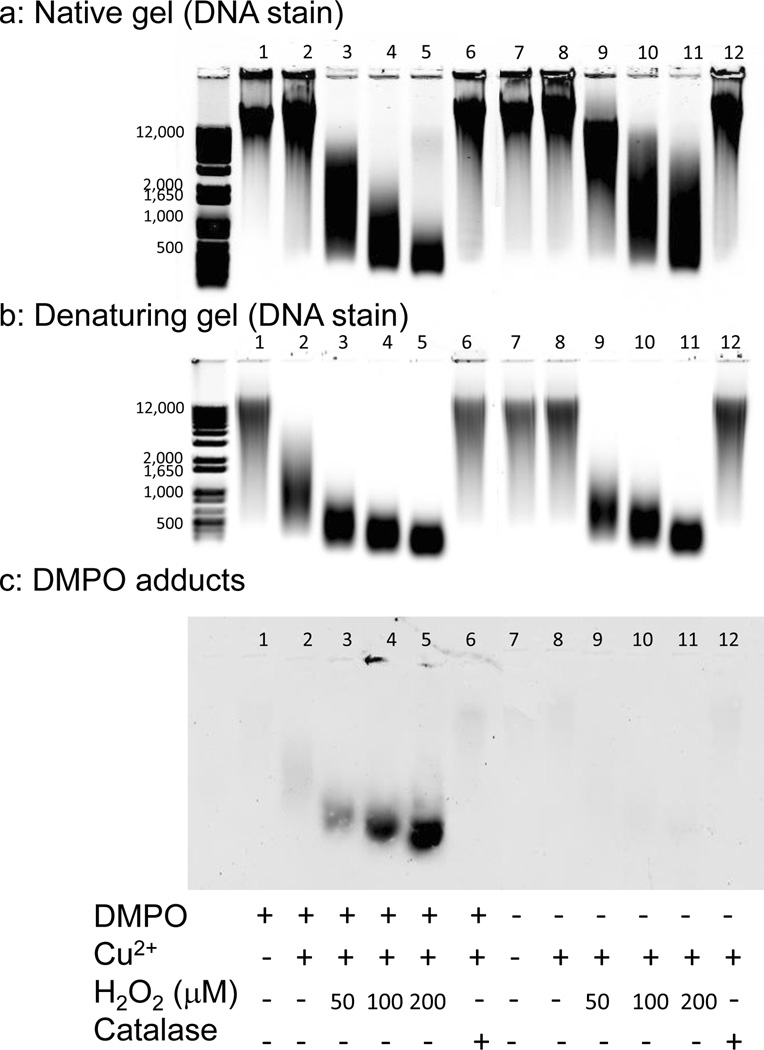
Figure 1.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA fragmentation under native and denaturing conditions and detection of DMPO adducts on DNA oxidized by Cu2+ and H2O2 in the presence and absence of DMPO. DNA (5 µg/lane) was electrophoresed on a 1% (wt/vol) agarose gel in TAE and stained with SYTO® 60 either under native conditions (panel a) or having been denatured in hot formamide prior to electrophoresis (panel b). Denatured DNA was transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane by capillary transfer and the DMPO adducts were detected using a monoclonal anti-DMPO adduct antibody (panel c). The DNA (250 µg mL−1) was treated with 50 µM Cu2+, 0–200 µM H2O2, 100 mM DMPO and 1 U mL−1 catalase as indicated. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments.