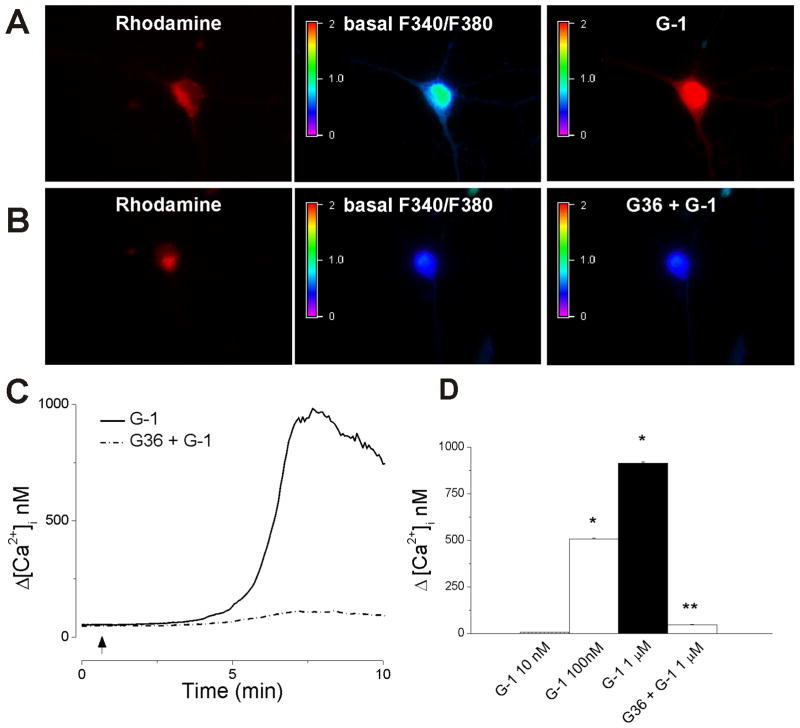
Fig. 1. Activation of GPER in cardiac vagal neurons of nucleus ambiguus increases cytosolic Ca2+.
A, Illustration of Fura-2 AM fluorescence ratio (F340/F380 nm) before (basal) and after G-1 treatment in cardiac preganglionic vagal neurons of nucleus ambiguus retrogradely labeled with rhodamine. B, Pretreatment with G36 prevented the increase in F340/F380 ratio produced by G-1. C, Representative recordings of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration, [Ca2+]i in response to G-1 in the absence (solid trace) and presence (dotted trace) of the GPER antagonist, G36. D, Comparison of increases in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration (Δ[Ca2+]i) produced by different concentrations of G-1 (10 nM - 1 μM) in the absence and presence of G36 (1 μM). *, P < 0.05 as compared to basal [Ca2+]i; **, P < 0.05, as compared to the increase in [Ca2+]i produced by G-1 (1μM).