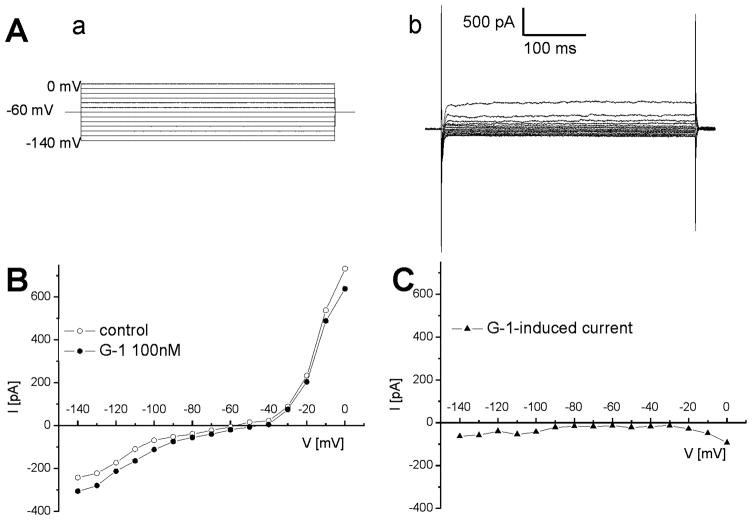
Fig. 3. G-1-induced inward current in nucleus ambiguus neurons.
A, Voltage steps (a) from −140 to 0 mV applied from a holding current of −60 mV induced currents (b) whose steady state values were used to construct current-voltage relationships. B, Representative example of steady state current values in response to voltage steps from −140 to 0 mV, before and after administration of G-1 (100 nM). C, Representative example of G-1-induced inward currents obtained by substraction of the IV curves obtained before and during perfusion with G-1.