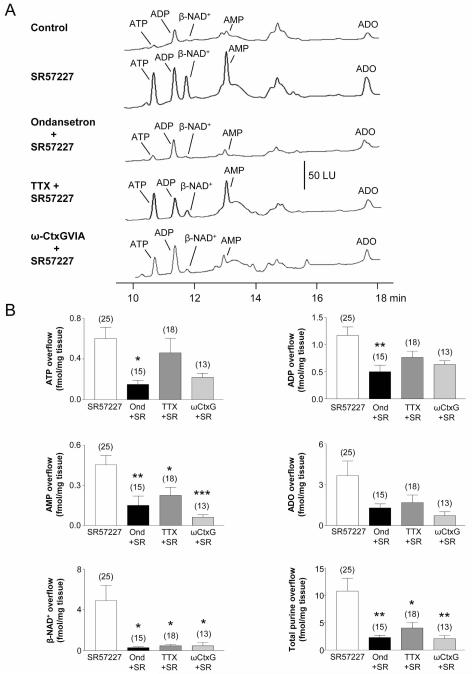
Fig. 4. Purines release by stimulation of 5-HT3 receptors in monkey colon whole muscle (WM) preparations.
(A) Chromatograms of tissue superfusates collected before (control) and during activation of 5-HT3 receptors with SR57227 (500 μM for 30 s) in the absence and presence of ondansetron (10 μM, 30 min), tetrodotoxin (TTX, 0.5 μM, 30-min superfusion) or ω-conotoxin GVIA (β-CtxG, 50 nM, 30-min superfusion) in monkey WM. Small amounts of ATP, ADP, β-NAD+, AMP and ADO were present in superfusate samples in the absence of agonist. Stimulation of 5-HT3 receptors with SR57227 evoked additional release of purines that was inhibited by the 5-HT3 receptor antagonist ondansetron. SR57227-evoked release of β-NAD+, but not ATP, was reduced by the neural blockers TTX and ω-CtxG. Scale applies to all chromatograms. LU, luminescence units. (B) Averaged data are means ± SEM and show release of ATP, ADP, AMP, ADO, β-NAD+ and total purines (calculated as ATP+ADP+AMP+ADO+β-NAD+) during activation of 5-HT3 receptors with SR57227 (SR) and in the presence of ondansetron (Ond, 10 μM, 30 min), TTX (0.5 μM, 30 min), and β-CtxG (50 nM, 30 min). Overflow (femtomoles per milligram of tissue) is the overflow during 5-HT3 receptor activation less spontaneous overflow. Each peak was calibrated to individual etheno-derivatized purine standards. Asterisks denote significant differences from SR57227-evoked release (i.e. control release) (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P<.001); number of experiments in parenthesis.