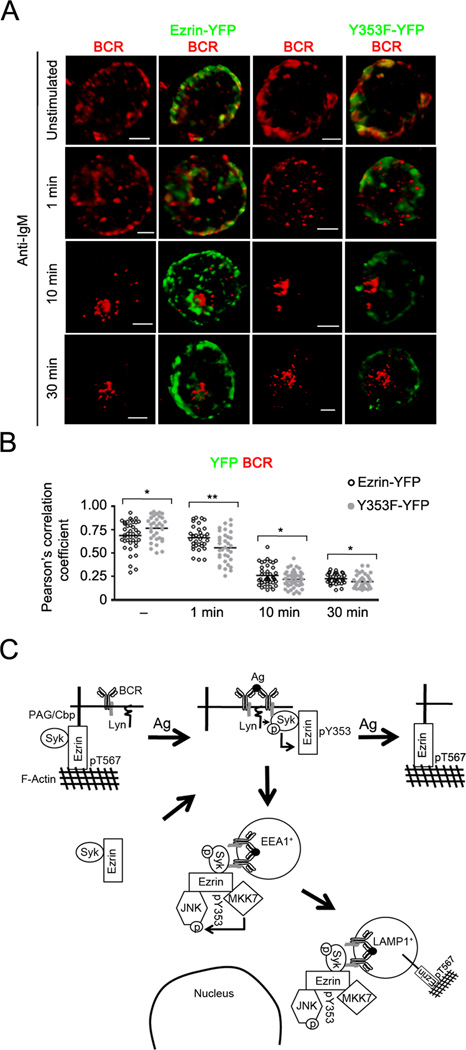
Figure 11. Y353F mutant of ezrin shows reduced co-localization with the internalized BCR.
(A) CH27 cells transfected with the Ezrin-YFP or Y353F-YFP fusion constructs of ezrin were stimulated with 10 µg/ml of anti-IgM for the indicated time, stained for BCR, and a z-stack of images was acquired. Volumetric renditions of representative cells from each stimulation time are shown. Scale bar, 5 µm. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (B) Pearson’s co-localization coefficients for YFP fusion protein and the BCR are shown. Each symbol represents an individual cell and horizontal lines indicate the mean (n=15–20 cells per group). (C) The model of endosomal regulation of BCR crosslinking-induced JNK activation by Y353-phosphorylated ezrin. Syk associates constitutively with a pool of either active, cortical ezrin bound to PAG, or inactive, cytosolic fraction of ezrin. Upon BCR ligation by antigen Lyn-mediated phosphorylation of the BCR ITAMs recruits Syk and Syk-associated ezrin, leading to Syk-dependent phosphorylation of ezrin at Y353. The Y353-phosphorylated ezrin associates with JNK and its kinase MKK7, and localizes them in the vicinity of the internalized BCRs that traffic within the early (EEA1+) followed by late endosomes (LAMP1+). The threonine phosphorylation of ezrin recovers within late endosomes at 30 min and at the plasma membrane between 20 and 45 min of BCR stimulation.