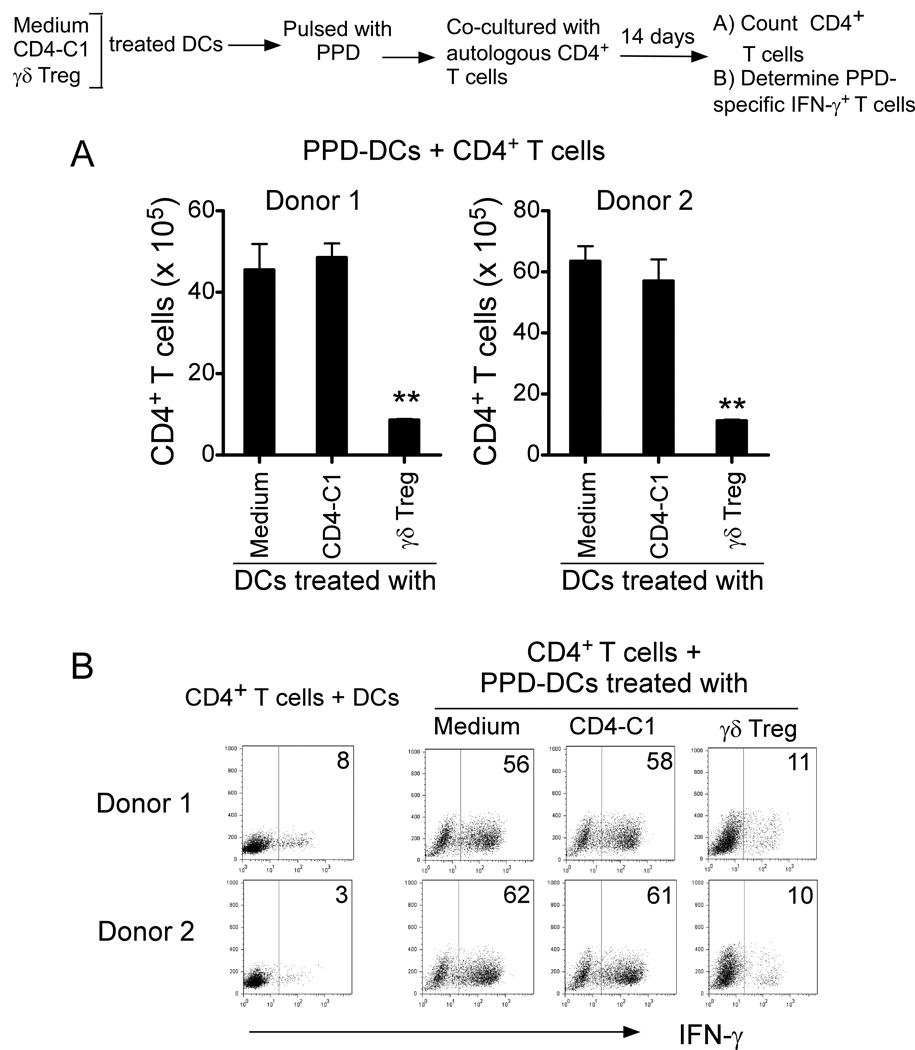
Figure 6. Senescent DCs induced by γδ Treg cells have impaired APC function to process and present antigen to T cells.
(A) γδ-Treg-induced senescent DCs pulsed with PPD had a weak ability to stimulate autologous T cell proliferation. However, PPD-pulsed DCs treated with or without CD4-C1 effector T cells strongly stimulated autologous T cell proliferation, resulting in up to 60-fold number increases. **p<0.01, compared with the DC groups treated with or without CD4-C1 T cells. (B) PPD-pulsed DCs treated with or without CD4-C1 T cells dramatically induced the increase of PPD-specific IFN-γ-producing T cell populations in the co-cultured T cells. In contrast, γδ Treg-induced senescent DCs as APCs only induced minor levels of PPD-specific IFN-γ-producing T cells. CD4+ T cells (1×105) purified from two healthy donors were co-cultured for 14 days with PPD-pulsed autologous DCs, which were pre-treated with medium, CD4-C1 or γδ Treg cells at ratio of 10:1. CD4+ T cell numbers were counted (in A). Furthermore, co-cultured CD4+ T cells were restimulated with PPD-pulsed autologous DCs for 2 days and IFN-γ-producing T cells determined by FACS analyses (in B).