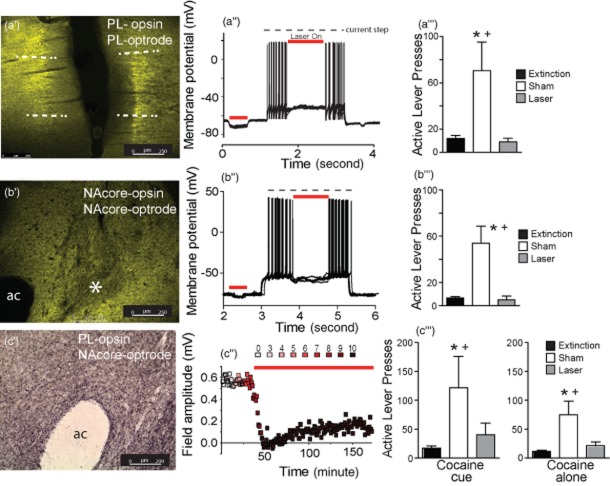
Figure 1.
Histological and electrophysiological verification of the opsin expression and inhibition of reinstated cocaine seeking. (a’) eNpHR3.0-YFP expression (green) after virus injection into the prelimbic cortex (PL). Dashed lines indicate approximate boundaries of the PL. (a’’) Laser-mediated hyperpolarization and inhibition of firing in a single eNpHR3.0-infected pyramidal cell. (a’’’) Laser light in the PL suppressed cocaine + cue-induced reinstated behavior. (b’) eNpHR3.0-YFP expression in the nucleus accumbens core (NAcore) after virus injection into the NAcore. ac, anterior commissure. *Area of relatively low fluorescence corresponding to the location of the fiber optic. (b’’) Laser-mediated hyperpolarization and inhibition of firing of a single eNpHR3.0-infected medium spiny cell. (b’’’) Laser light into the NAcore suppressed reinstated behavior. (c’) Immunostaining of archaerhodopsin expression in axonal fibers the NAcore after virus injection into the PL. (c’’) Optical inhibition of field potentials recorded in NAcore after electrical stimulation in the eNpHR3.0-infected PL of a rat. Units of laser intensity are arbitrary and correspond to step increases until the field potential disappeared and remained at this intensity for the duration of the experiment. (c’’’) Laser illumination in the NAcore suppressed both cocaine- and cocaine + cue-induced reinstatement.