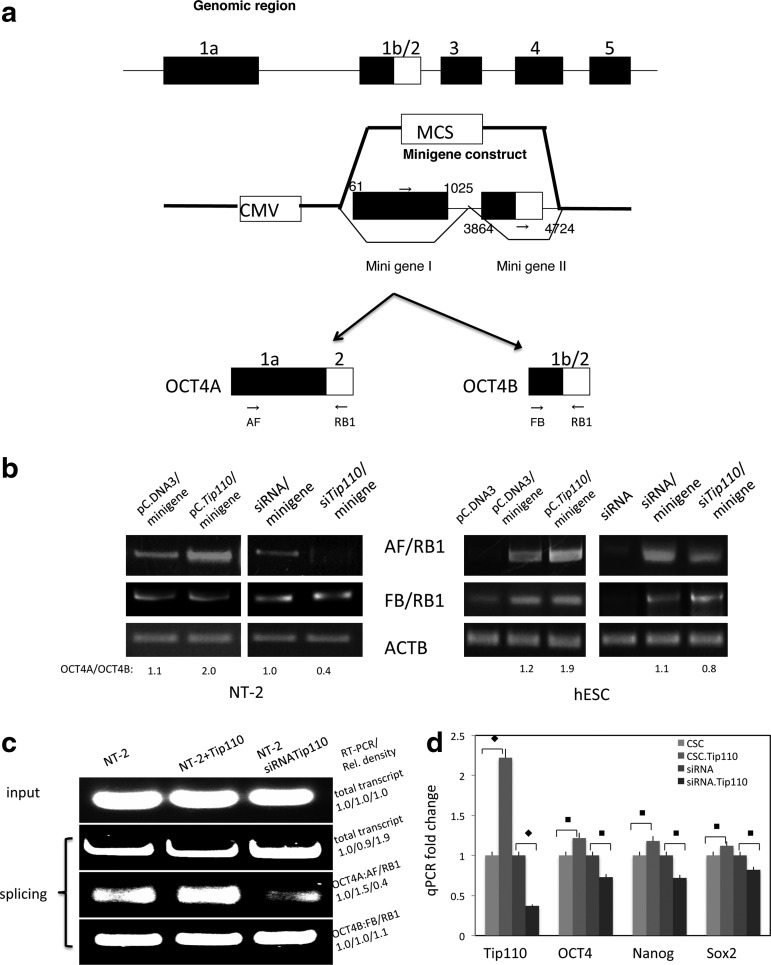
FIG. 4.
Human OCT4 genomic schematic organization, OCT4 minigene construct, and RT-PCR analysis of OCT4A transcripts. (a) Two fragments of the OCT4 genomic clones spanning OCT exon 1 and exon 2 were amplified by PCR, then they are cloned into pCDNA3 vector multiple cloning sites (MCS), which could be spliced with either OCT4A and/or OCT4B. (b) Coexpression of plasmids for pC.DNA3 (control) and pC.DNA3TIP110; and shRNA (control) and shRNA.TIP110 with OCT4 minigene in NT-2 cells and H9 hESCs. Cells were harvested 48 h after transfection for OCT4A and OCT4B mRNA expression by RT-PCR. OCT4A/OCT4B ratio was calculated through densitometry reading. β-actin was used as a loading control. (c) OCT4 minigene was in vitro transcribed into pre-mRNA. The OCT4 minigene transcribed pre-mRNAs were incubated with NT-2 cell extract (L1), NT-2 cell extract plus recombinant TIP110 protein (L2), and NT-2 cell with siRNA for TIP110 extract in splicing buffer for 0 hrs (input) or 3 hrs reaction at 30°C. RNAs were extracted from the input for quantitative RT-PCR of total transcript; quantitative RT-PCR for total transcript, OCT4A, and OCT4B from splicing reactions. (d) The stem cell markers (OCT4, Nanog, and Sox2) were analyzed in NT-2 cells by qPCR with overexpressing TIP110 or silencing the expression. β-actin was used to normalize q-PCR results. Data in panel d are expressed as mean±SD of 3 independent experiments. ♦P<0.05; ■P<0.001 for the compared pair.