Fig. 3.
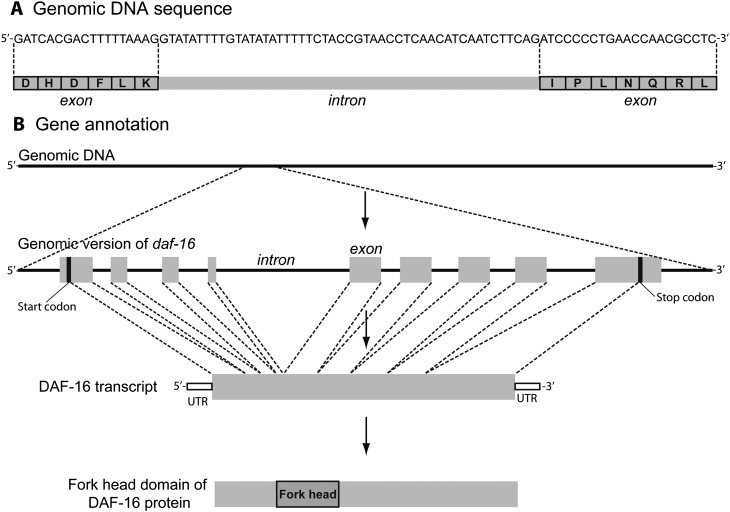
Gene annotation. A) An overview of gene architecture, showing a stretch of DNA demarcated into protein-coding exons and non-coding introns. B) An example of gene annotation, proceeding from identification of genes from the genome either predicted de novo from gene-like patterns in the sequence or by comparison to known genes. In this case, the daf-16 gene is shown with its introns and exons. Below that is a transcript from the daf-16 gene, with the open reading frame (ORF) along with the upstream and downstream untranslated regions (UTR). The genome is also scanned for known protein domains; in this case, daf-16 has a single protein domain, although other proteins may contain several domains.