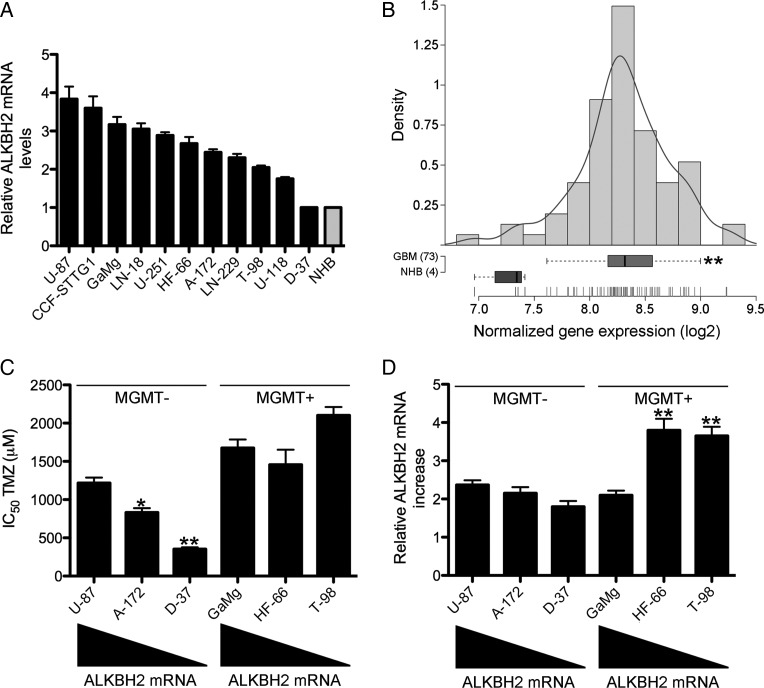
Fig. 1.
ALKBH2 expression in GBM cells and human GBM. (A) ALKBH2 mRNA expression in a panel of 11 DNA fingerprinted GBM cell lines compared with NHB determined by qRT-PCR. (B) ALKBH2 gene expression (Affymetrix probe 225625_at) in 4 NHB samples and in 73 newly diagnosed GBM obtained from a previously published data set.12 Recurrent GBM was excluded in the analysis. **P < .01. (C) Correlation between ALKBH2 mRNA expression levels and temozolomide sensitivity in MGMT-deficient (U87, A172, and D37) and MGMT-proficient (GaMg, HF66, and T98) GBM cell lines. *P < .05, **P < .01. (D) Levels of ALKBH2 induction in GBM cell lines with distinct baseline ALKBH2 expression and MGMT status were quantified by qRT-PCR following 24h of temozolomide (TMZ) exposure with each cell line's corresponding half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) dosage. The increase in ALKBH2 mRNA in cells receiving temozolomide was calculated relative to corresponding control cells treated with drug vehicle (DMSO) only. **P < .01.