Fig. 2.
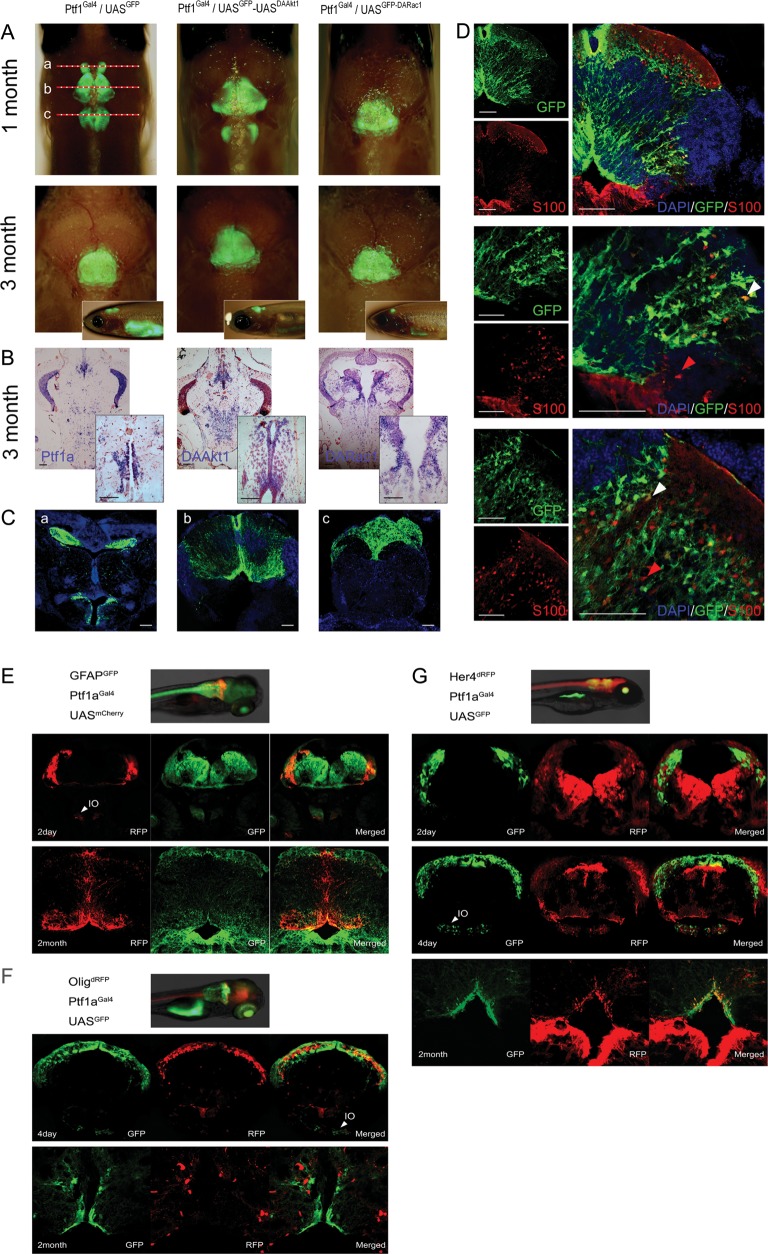
Transgene expression in juvenile and adult zebrafish. (A) Merged bright and fluorescence images showing GFP expression at the cerebellum and medulla. Depigmented phenotypes were obtained by successive crossing with the mitfaw2;roya9 line. Although 1-month-old zebrafish showed sustained GFP expression at the cerebellum and medulla, transgene expression was more localized at the cerebellum at 3 months. The top is anterior. Inlets are lateral views. (B) ISH for Ptf1a and transgenes. Transgene expression is stronger at the intermediate layer and the ventricular zone. Inlets are enlarged views of the ventricular area. (C) Coronal images of 1-month-old Ptf1aGal4/UASGFP zebrafish of (A). (b) GFP expression is robust along the midline and at the dorsal lining of the fourth ventricle. (D) Immunofluorescence for S100 at the similar plane level of (Cb). S100-positive cells are concentrated at the ventral lining of the fourth ventricle and the intermediate layer and scattered in the granular layer. Strong Ptf1a expression (GFP) persists in cells at intermediate layer, ventricular zone, and along the midline. Images reveal cerebellar cells positive for either GFP or S100 (red arrowheads) alone or for both (white arrowheads). (E–G) Coexpression analyses. During embryonic development, Ptf1a expression is noted in cells at the dorsum of cerebellum and inferior olive nucleus (IO). (E) GFAPGFP/Ptf1aGal4/UASmCherry zebrafish. Most cells expressing Ptf1a (RFP) also express GFAP (GFP). (F) Olig2dRFP/Ptf1aGal4/UASGFP zebrafish. Cerebellar cells do not coexpress Olig2 and Ptf1a both in embryo and adult. (G) Her4dRFP/Ptf1aGal4/UASGFP zebrafish. During embryonic development, ptf1a-positive cells (GFP) are at just underneath Her4-expressing (RFP) cells and rarely coexpress Her4. In adults, Ptf1a-positive cerebellar cells at ventricular and supraventricular areas occasionally coexpress both Ptf1a and Her4. Bars, 50 μm.