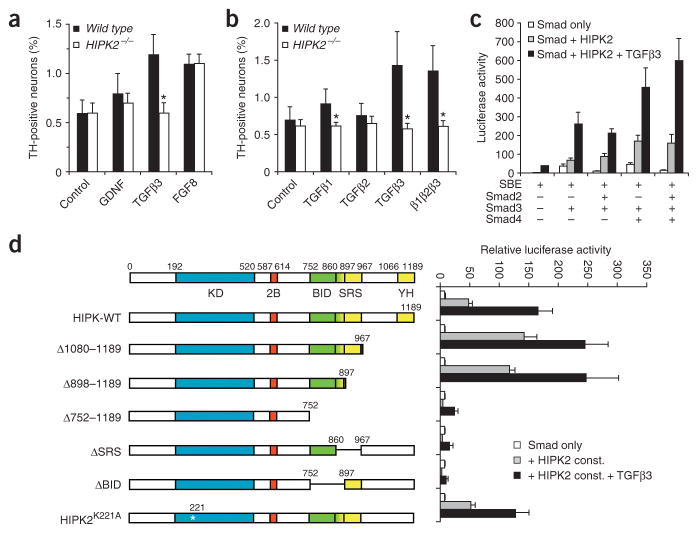
Figure 7.
HIPK2 is important in the TGFβ-Smad signaling pathway. (a) DA neurons from the ventral mesencephalon of E13.5 embryos are cultured in the defined medium. DA neurons lacking HIPK2 fail to survive in the presence of TGFβ3, but survive in the presence of FGF8 or GDNF. (b) Among the three TGFβ isoforms, TGFβ3 shows the most potent effect in supporting cultured DA neurons, whereas TGFβ1 shows a very modest effect and TGFβ2 has no detectable effect. Statistical analyses for panels a and b use Student’s t-test, n = 4 for wild-type and n = 5 for Hipk2−/− mutants. * indicates P < 0.05.
(c) HIPK2 enhances the ability of R-Smads, especially Smad3, to activate luciferase reporter SBE in HEK293 cells. The coactivator effect of HIPK2 is further enhanced by TGFβ3 (5 ng ml−1). (d) Deletion of the Brn3a-interaction domain (ΔBID), speckle-retention domain or both (Δ752–1189) completely abolishes the coactivator effect of HIPK2 in SBE luciferase assays in HEK293 cells. In contrast, loss of the co-repressor domain in the C-terminus (Δ1080–1189 or Δ898–1189) leads to a slight increase in the SBE activity. Point mutation of the conserved lysine residue in the ATP binding pocket, HIPK2K221A, does not affect the activity of HIPK2 in SBE luciferase assays. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments.