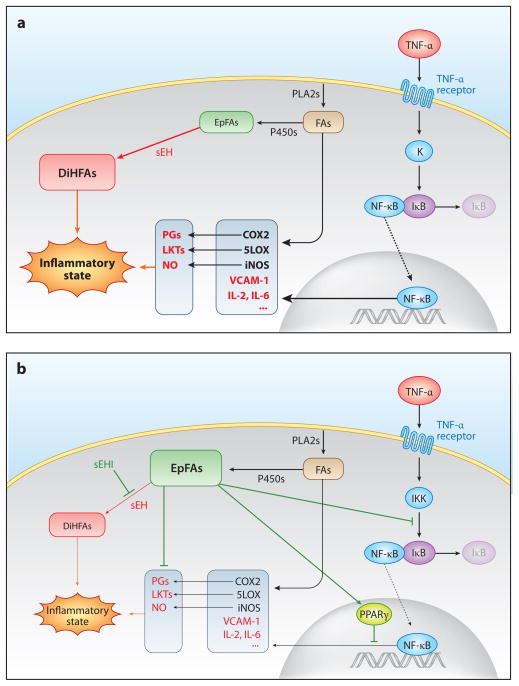
Figure 3.
(a) Role of epoxy-fatty acids (EpFAs) in inflammation. (b) Effects of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors (sEHIs). Abbreviations: COX, cyclooxygenase; DiHFA, 1,2-dihydroxy-fatty acid; FA, fatty acid; IKK, IκB kinase; IL, interleukin; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; LKT, leukotriene; LOX, lipoxygenase; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; NO, nitric oxide; PG, prostaglandin; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; sEH, soluble epoxide hydrolase; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1.