Figure 4. Frequencies of most significant markers (based on the logistic regression test) in GWAS based on genotyping panels of previously ascertained SNPs.
(a) From our simulated case-control studies, we randomly-sampled markers in order to mimic the ascertainment of common markers typical of current GWAS, which resulted in a uniform distribution of minor allele frequencies. The distribution shown here is summed across all replicate simulations of a gene region. (b–f) Monte Carlo estimates of the expected number of most-associated markers in different frequency intervals for different values of λ (the mean effect size of a causative mutation). The x-axis represent the frequency of the minor allele (defined in the general population) in the cases. In each panel, 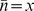 is an estimate of the expected number of replicates (out of a total of 250) containing at least one significant marker using an imperfect SNP chip.
is an estimate of the expected number of replicates (out of a total of 250) containing at least one significant marker using an imperfect SNP chip.

