Figure 2. Map-based cloning of Ehd4.
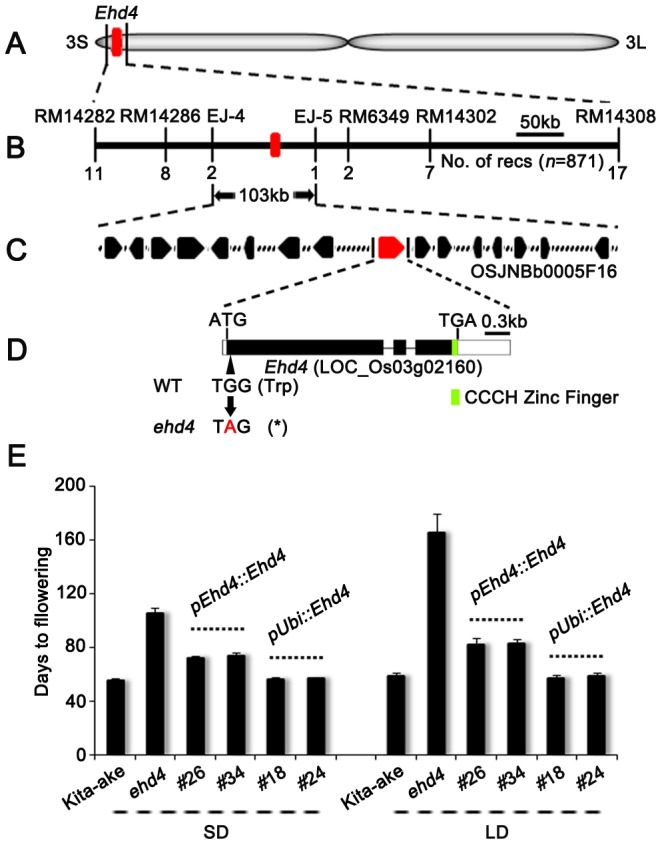
(A) Location of the Ehd4 locus on rice chromosome 3. (B) High-resolution linkage map of Ehd4. (C) Candidate genes on BAC OSJNBb0005F16. (D) Structure of the Ehd4 gene. Lines, black and white boxes represent introns, exons and untranslated regions, respectively. The base change from G to A creates an early stop codon (Asterisk). (E) Complementation of ehd4. Ehd4 was driven by either the native promoter (pEhd4::Ehd4) or the maize Ubiquitin-1 promoter (pUbi::Ehd4). T2 plants of two pEhd4::Ehd4 lines (#26 and #34) and two pUbi::Ehd4 lines (#18 and #24) were measured (n = 10). All plants were grown under both SD and LD conditions.
