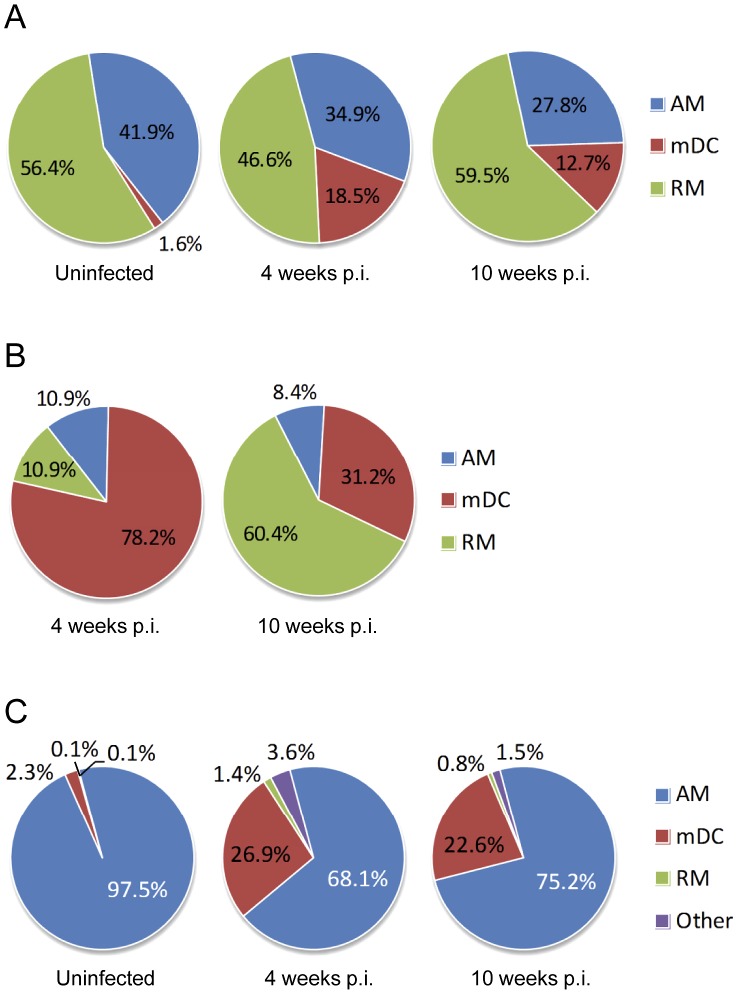
Figure 1. Distribution of Mtb infection within monocytic cell populations in the lung.
Whole lung leukocytes were harvested from groups of mice with TB (4 and 10 weeks p.i.) and compared to uninfected controls. Monocytic cells were sorted into AM, RM and mDC as described in Materials and Methods. Ziehl-Neelsen staining was performed on cytospin preparations of sorted populations. (A) The proportion of AM, RM and mDC within the total lung monocytic cell population of uninfected mice and mice with pulmonary TB. (B) The proportion of AM, RM and mDC containing any AFB in mice with pulmonary TB. (C) The proportion of GFP-labeled lung leukocytes, GFP+ AM, RM and mDC, in uninfected mice and mice with TB. Lung leukocytes within the airspace were transduced by tracheal instillation of WT mice with CMV-GFP-W. After 8 weeks, one group of GFP-transduced mice was challenged by aerosol with 300 CFU of Mtb Erdman delivered to the lung. The category Other comprised cells that could not be categorized as AM, RM or mDC based on light scatter characteristics and CD11b/CD11c staining. By light microscopy, cells in the Other category included a small number of neutrophils that may have acquired GFP by efferocytosis, as well of cells with monocytic appearance that had very high intracellular Mtb burden and features of cell death. Monocytic cell subsets were classified by surface immunostaining as alveolar macrophages (AM; CD11b− CD11c+/hi), recruited monocyte/macrophages (RM; CD11b+/lo CD11clo/−) and myeloid dendritic cells (mDC; CD11b+/hi CD11c+/hi).