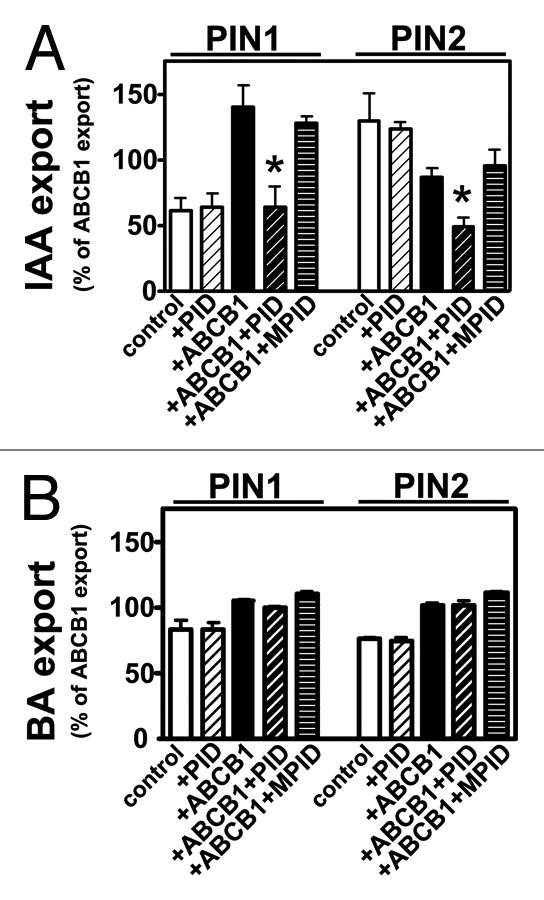
Figure 1. PID modulates PIN-mediated auxin efflux in yeast. (A) PID has no significant impact on PIN-mediated auxin (IAA) export but specifically inhibits ABCB1/PIN1- and ABCB1/PIN2-mediated IAA export not seen with MPID. Note that PIN1 in the absence of ABCB1 is inactive in the yeast, S. cerevisiae.13(B) PID modulation of ABCB and PIN-mediated IAA export is specific. PID and a mutated, inactive PID (MPID) have no significant influence on PIN1-, PIN2-, ABCB1/PIN1- or ABCB1/PIN2-mediated benzoic acid (BA) export. Reduction of IAA and BA retention (efflux) were calculated as relative export of initial export where ABCB1 was set to 100% (mean ± SE; n = 4–10). Significant differences (unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction, p < 0.05) between –PID controls are indicated by asterisks.
