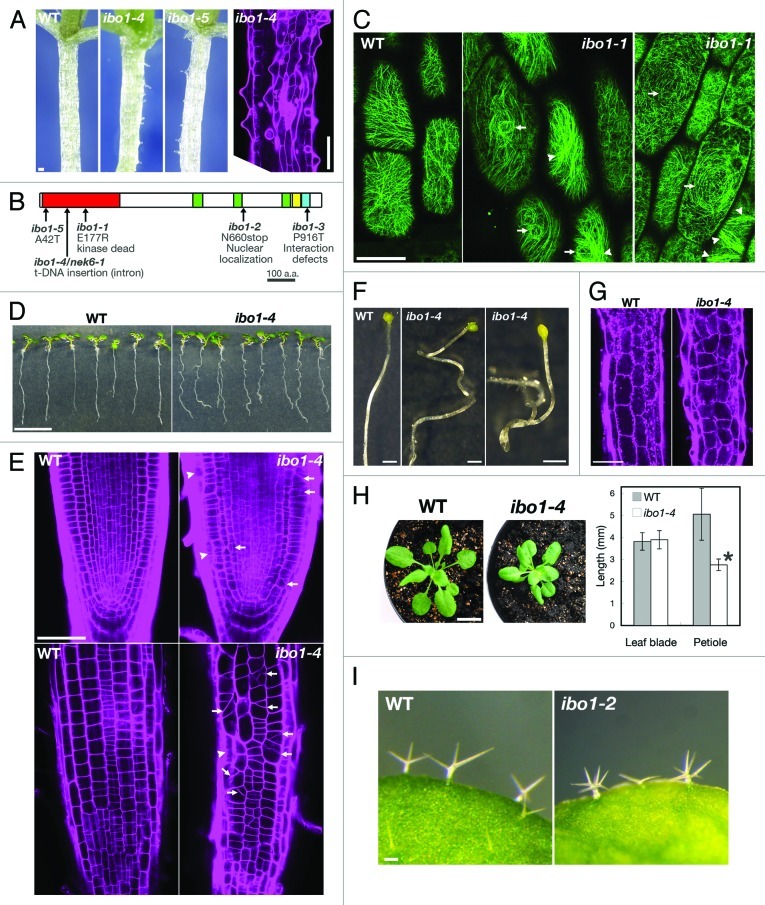
Figure 1. The nek6/ibo1 mutants exhibit disorganized cell growth. (A) Morphology of hypocotyls of 10-d-old seedlings of the wild type (WT) and ibo1. The right part shows a hypocotyl of ibo1–4 stained with propidium iodide. (B) Structure of NEK6. PEST sequence (green), coiled-coil domain (yellow), plant NEK C-terminal motif (blue) and mutation sites are shown. (C) Cortical microtubules were visualized with GFP-TUB6 in hypocotyl epidermal cells of the wild type (WT) and ibo1–1. Arrows and arrowheads in (C) indicate whirled arrays of microtubules and microtubule bundles, respectively. (D and E) Morphology of the wild type (WT) and ibo1–4 seedlings grown vertically for 7 d. (E) Seedlings were stained with propidium iodide and root tips were observed under a confocal microscope. Median longitudinal optical section (upper parts in E) and epidermis (lower parts in E) of root tip were shown. Arrows and arrowheads indicate aberrant cell plates and irregular cell files, respectively. (F) Morphology of hypocotyls of the wild type (WT) and ibo1–4 grown in the dark for 7 d. (G) Hypocotyl cortex of the wild type (WT) and ibo1–4. Seedlings grown in the light for 7 d were stained with propidium iodide and observed under a confocal microscope. (H) Morphology of 4-week-old wild type (WT) and ibo1–4 plants (left parts) and quantification of lengths of leaf blades and petioles of 14-d-old seedlings (right parts). Values are means ± SD (n = 10). Asterisk indicates significant difference from the wild type (Student t-test, p < 0.01). (I) Trichomes of the wild type (WT) and ibo1–4. Bars = 100 µm (A, G and I), 50 µm (C and E), 10 mm (D and H) or 1 mm (F).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.