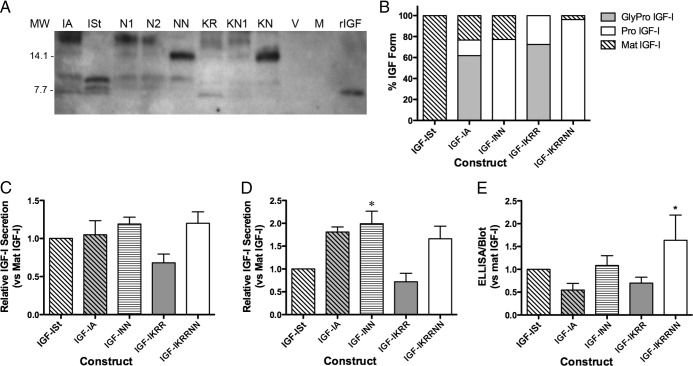
Figure 3.
Secretion of IGF-I Forms after Transient Transfection of IGF-I Constructs. A, Immunoblot detection of the IGF-I forms secreted (30 μL media per lane). IA, transfection of wild-type IGF-IA; ISt, IGF-ISt transfection; N1, transfection of IGF-IA with N92A mutation; N2, transfection of IGF-IA with N100A mutation; NN, transfection of IGF-IA with N92A/N100A mutation; KR, blockade of cleavage site between mature IGF-I and the E-peptide; KN1, blockage of cleavage and N92A mutation; KN, blockade of both cleavage and glycosylation; V, vector only; M, mock transfection. B, The proportion of IGF-I forms secreted after transient transfection. C, ELISA measurements of IGF-I secreted after transient transfection. Data are presented as IGF-I levels normalized to that in media from mature IGF-I transfections for four experiments. D, Quantification of total IGF-I secreted after transient transfection based on immunoblot. *P < .05 significantly different compared with mature IGF-I. E, Ratio of ELISA and immunoblot quantification shows that presence of glycosylation causes an underestimation of IGF-I by ELISA. Data are presented as the sum of all IGF-I bands produced by each construct normalized to bands from transfection of mature IGF-I in four experiments. *P < .05 significantly different compared with mature IGF-I. MW, molecular weight.