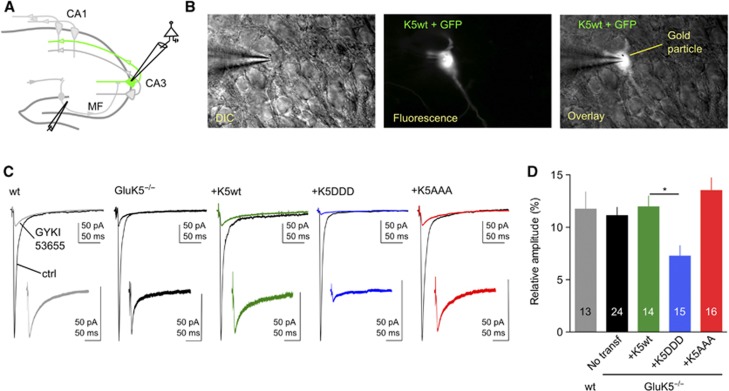
Figure 7.
CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of GluK5 regulates synaptic KARs. (A) Schematic cartoon of the hippocampus illustrating a cell co-transfected with GFP and the gene of interest. (B) Example images of a CA3 pyramidal cell co-transfected with GFP and GluK5wt. (C) Voltage-clamp recordings were performed on GFP-expressing pyramidal cells at −70 mV in the presence of bicuculline (10 μM), D-AP5 (50 μM) and a low concentration of NBQX (150 nM) to limit polysynaptic activity. In all, 30 responses evoked at 3 Hz were averaged in the absence and in the presence of 50 μM GYKI53655, to isolate the AMPAR and the KAR component of the mf-CA3 synaptic response, respectively. In the insert are showed enlargements, by the same proportion, of isolated KAR-EPSCs. (D) Summary of the results of the relative amplitude of KAR-EPSCs versus AMPAR-EPSCs after transfection with either WT or mutated GluK5 subunits (wt: 11.8±1.4%, n=13; GluK5−/−: 11.1±0.8%, n=24; GluK5−/−+GluK5wt: 11.9±1.0%, n=14; GluK5−/−+GluK5DDD: 7.2±0.9%, n=15; GluK5−/−+ GluK5AAA:13.5±1.2%, n=16). Values are presented as mean±s.e.m. of n experiments. Data were compared using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (*P<0.005).