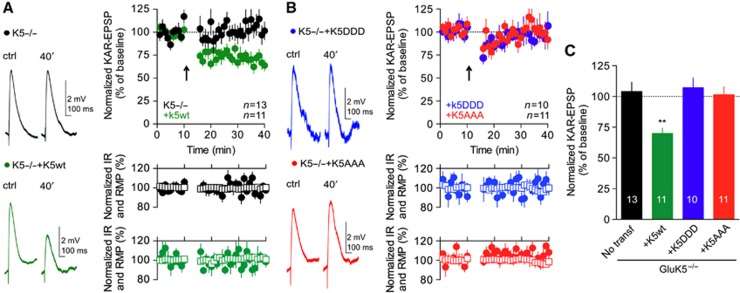
Figure 8.
Phosphorylation of GluK5 is responsible for CaMKII-dependent KAR-LTD. (A) In slices prepared from GluK5−/− mice, re-expression of GluK5wt restored KAR-LTD. Representative traces of current-clamp recordings of KAR-EPSPs before and after the pairing protocol, in GluK5−/− and after transfection with GluK5wt. Input resistance (empty squares) and resting membrane potential (filled circles) remained stable throughout the experiment. (B) KAR-LTD was not observed in cells transfected with the GluK5DDD or GluK5AAA. Representative traces of KAR-EPSPs before and after the pairing protocol, after transfection with GluK5DDD or GluK5AAA. (C) Summary of the changes of KAR-EPSP amplitudes after STDP-like protocol in slices prepared from GluK5−/− mice, and after transfection with WT or mutated GluK5 subunit (GluK5−/−: 104.1±7.5%, n=13; GluK5−/−+GluK5wt: 69.9±4.3%, n=11; GluK5−/−+GluK5DDD: 107.2±7.9%, n=10; GluK5−/−+GluK5AAA: 101.4±6.5%, n=11). Values are presented as mean±s.e.m. of n experiments. Data were compared using unpaired t-test (**P<0.001).