Figure 5.
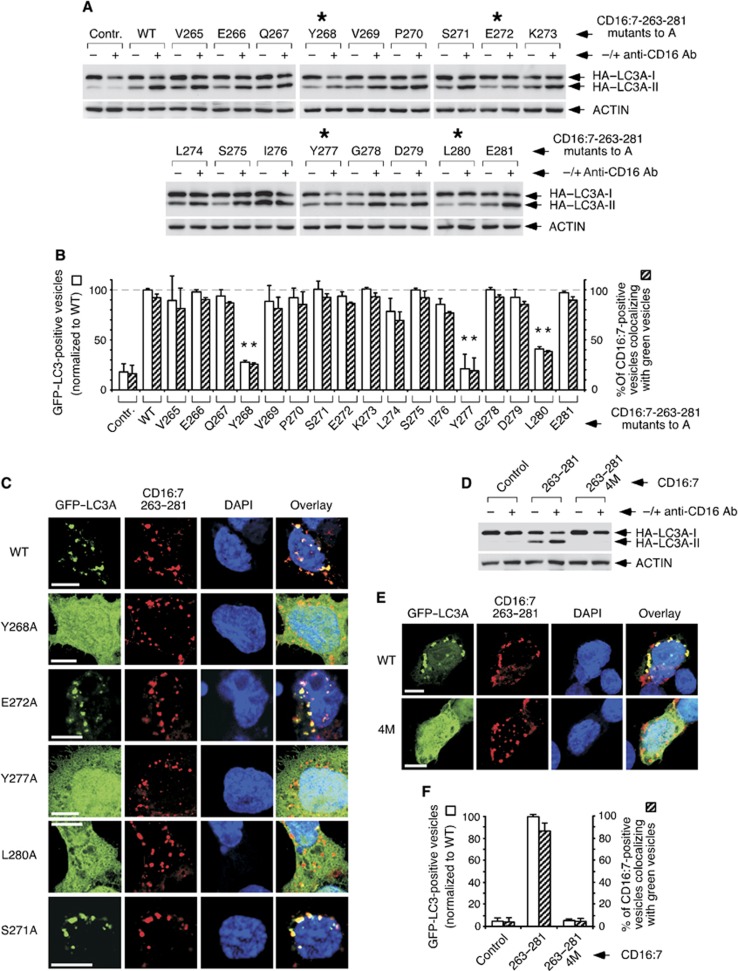
Alanine scanning approach to identify amino acids in the active subdomain of TMEM59 that are essential for LC3 activation. (A) Identification of critical amino acids for HA–LC3 conversion. 293 cells were transfected with the indicated CD16:7–263–281 mutants and HA–LC3A, subjected to anti-CD16 aggregation and lysed for western blotting against the indicated molecules. Asterisks mark mutations with reduced activity. Shown is one representative experiment of six repetitions. (B) Identification of critical amino acids for GFP–LC3 activation and colocalization with the endocytosed chimera. JAR cells were transfected with the indicated CD16:7–263–281 mutants and GFP–LC3A, aggregated and stained for the endocytosed chimera (red). Preparations were scored by blindly counting the number of red vesicles (chimera) and green vesicles (GFP–LC3A) per cell, as well as the number of red vesicles colocalizing with green ones. The percentage of green vesicles colocalizing with red ones was close to 100% for all mutants, that is, virtually no GFP–LC3A vesicles were unrelated to endocytosed chimera (not shown). At least 50 cells were scored per experimental point. The experiment was repeated three times. The graph shows the number of GFP–LC3A vesicles per cell expressed as the percentage of the value obtained for the wild-type chimera (left axis), and the percentage of chimera vesicles labelled with GFP–LC3A (right axis). Data are expressed as means ±s.d. of the triplicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences with respect to wild-type values (paired Student’s t-test; P<0.01). (C) Representative confocal pictures of the phenotype produced by the indicated mutations. Procedures were as in B. (D) Simultaneous mutation of the four essential amino acids to alanine blocks HA–LC3 conversion induced by CD16:7–263–281. 293 cells were transfected with the indicated chimeras (4M, quadruple mutant) and HA–LC3A, aggregated and lysed for western blotting. (E) Simultaneous mutation of the four essential amino acids blocks GFP–LC3 activation and colocalization with the endocytosed chimera. JAR cells were transfected with the indicated CD16:7–263–281 constructs and GFP–LC3A, aggregated and stained for the endocytosed chimera (red). Representative confocal images are shown. (F) Quantification of the phenotype in E. Data gathering and expression were as in B.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.