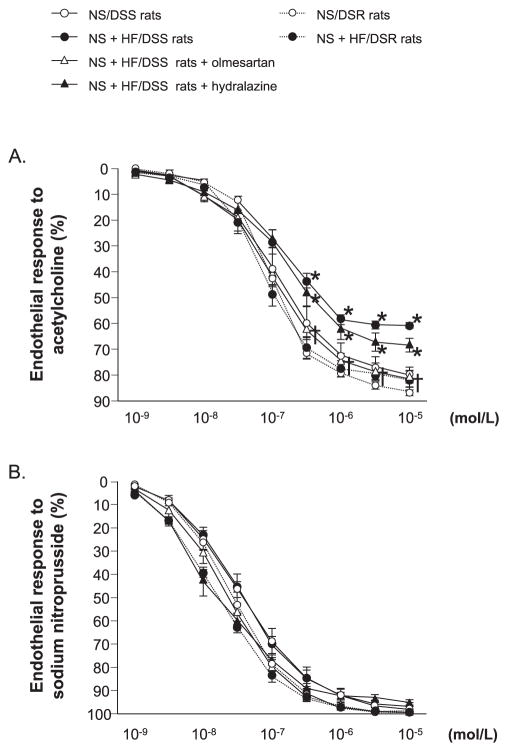
Fig. 2.
Dose–response curve for acetylcholine (A)- and sodium nitroprusside (B)-induced vasorelaxation of the thoracic aorta. Acetylcholine-induced relaxation was significantly reduced in NS + HF diet–fed DSS rats. In these animals, impairment of acetylcholine-induced relaxation was normalized by treatment with olmesartan but not with hydralazine. Sodium nitroprusside–induced vasorelaxation was not different among the groups. *P < 0.05: NS/DSS rats vs. NS + HF/DSS rats, NS + HF/DSS rats + olmesartan or NS + HF/DSS rats + hydralazine; †P < 0.05: NS + HF/DSS rats vs. NS + HF/DSS rats + olmesartan or NS + HF/DSS rats + hydralazine.