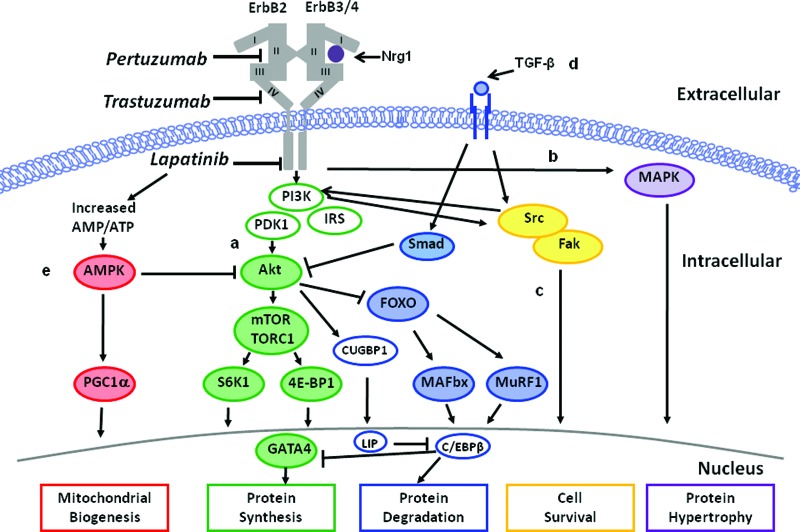
Figure 1.
Mechanisms underlying HER2-directed therapy cardiotoxicity. Inhibition of ErbB receptors with HER2-directed therapies impacts numerous signaling pathways resulting in suppression of myofilament protein synthesis via the PI3K-Akt pathway (pathway A), suppression of protein hypertrophy via the MAPK pathway (pathway B), suppression of cell survival via Src/Fak pathway (pathway C), suppression of myofilament protein synthesis and upregulation of protein degradation via TGF-β1 and C/EBPβ signaling (pathway D), and alterations in cardiac energy metabolism via downregulation of AMPK (pathway E).
Abbreviations: AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; C/EBPβ, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein; Fak, focal adhesion kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; Nrg1, Neuregulin-1β; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Smad, small mother against decapentaplegic; TGFβ, transforming growth factor β.