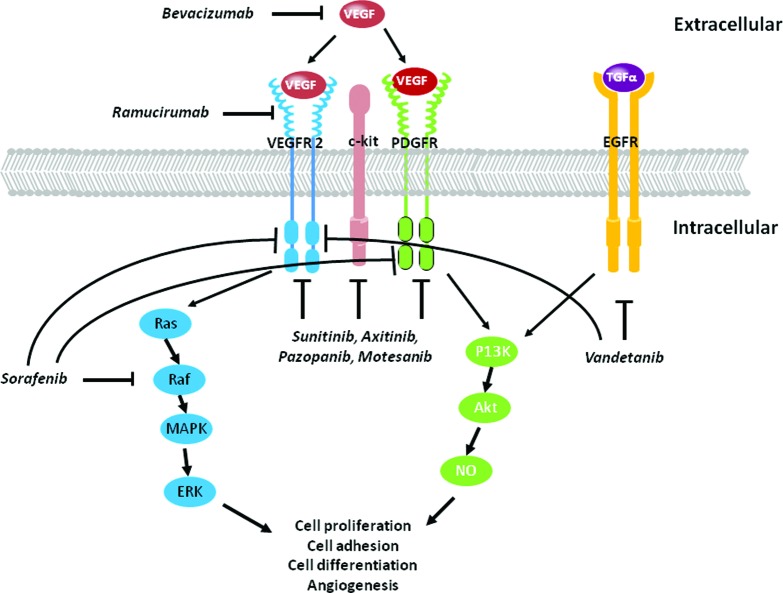
Figure 3.
Mechanisms underlying anti-angiogenic therapy cardiotoxicity. Inhibition of VEGF signaling with tyrosine kinase inhibitor-directed therapies impacts numerous signaling pathways resulting in inhibition of angiogenesis, and protein synthesis and degradation via the PI3K-Akt-NO pathway; and inhibition of cell proliferation and differentiation via the MAPK-ERK pathway. Monoclonal inhibitors include bevacizumab and ramucirumab; multikinase inhibitors include sunitinib, axitinib, pazopanib, motesanib, vadetanib, and sorafenib.
Abbreviations: MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NO, nitric oxide; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.