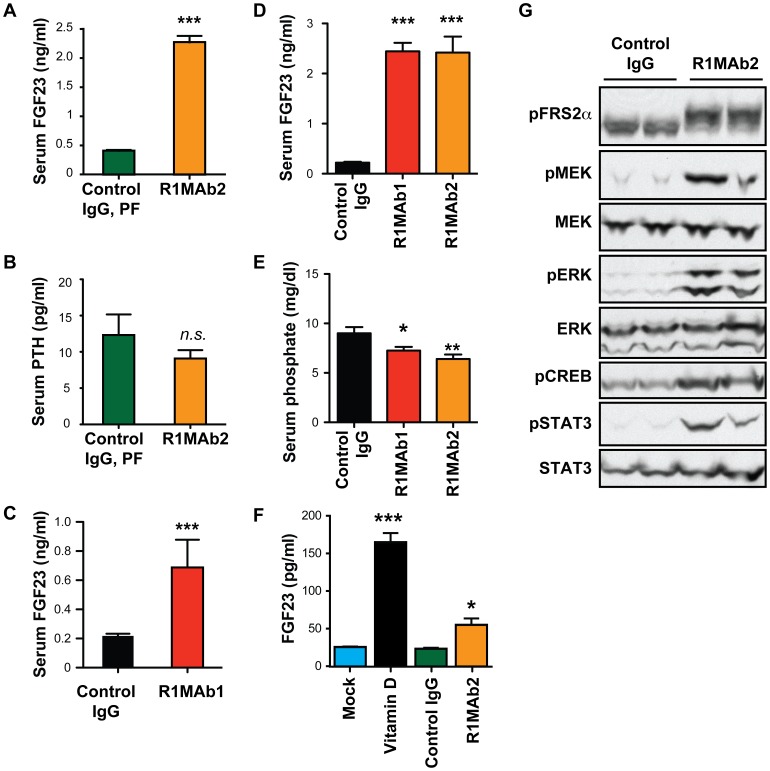
Figure 3. R1MAb2 induces FGF23 production.
(A and B) Serum FGF23 (A) and PTH (B) levels in male C57BL/6 mice intraperioneally injected with R1MAb2 or isotype control (Control IgG) at 1 mg/kg. The same animals described in Figure 1C and Figure 2 were analyzed at 48 hour post injection. N = 8 mice/group. (C) Serum FGF23 levels in female db/db mice intraperioneally injected with R1MAb1 or isotype control (Control IgG) at 2 mg/kg. The samples were collected at 7 days post injection. N = 6 mice/group. (D and E) Serum FGF23 levels (D) and phosphate levels (E) in male C57BL/6 mice intraperioneally injected with an indicated antibody at 1 mg/kg. The samples were collected at 3 days post injection. N = 8 mice/group. (F) FGF23 levels in culture medium after treatment of differentiate rat osteoblast with vitamin D (100 nM), R1MAb1, or isotype control IgG (26.7 nM). The cells were incubated for 48 hours in the presence of the indicated ligand. N = 6 samples/treatment. (A–F) * p<0.05, **<p<0.005, ***<p<0.0005. (G) Differentiated rat osteoblasts were treated with R1MAb2, or isotype control IgG (26.7 nM), for 1 hour and subjected to Western blot analysis to examine phosphorylation of MAPK pathway proteins, CREB and STAT3.