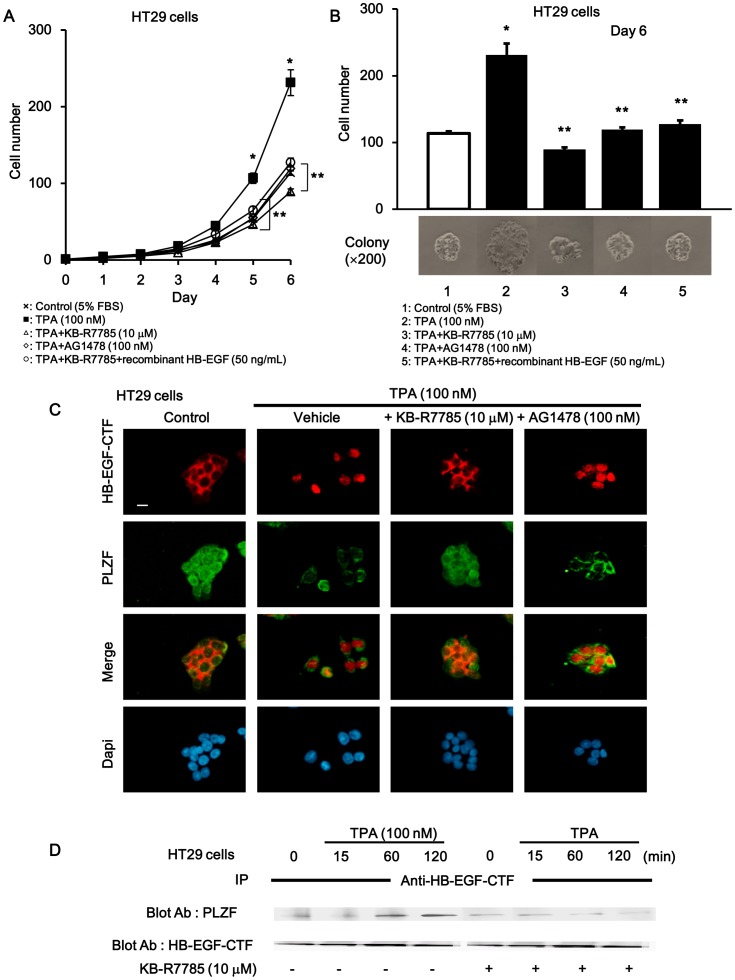
Figure 6. Cell proliferation through EGFR pathway and nuclear translocation of HB-EGF-CTF during TPA stimulation.
TPA-induced cell proliferation through EGFR and nuclear translocation of HB-EGF-CTF signaling. (A) Growth curve assay. HT29 cell numbers which were counted daily, 24 h (i.e.day1) after cells were seeded in three dependent colonies that were cultured in conditioned media. The values are means of three independent experiments. (B) Cell numbers of colonies cultured in 5% FBS conditioned media with or without TPA, KB-R7785, AG1478, and recombinant HB-EGF on day6. The cells were also observed with microscopy (×200) *P <0.05 for the stimulus effect, and **P<0.05 for the inhibitory effect. (C) Effects of KB-R7785 and AG1478 on TPA-induced nuclear translocation of HB-EGF-CTF and nuclear export of PLZF. Cells were treated with TPA following preincubation with or without KB-R7785 and AG1478. Immunofluorescent staining with anti-HB-EGF-CTF antibodies (red signals), anti-PLZF antibodies (green) and DAPI (blue), which stains for nuclei was performed. Images were obtained on a fluorescence microscope (×200). The white bar indicated 10 µm. (D) Effects of KB-R7785 on the association between HB-EGF-CTF and PLZF after TPA stimulation. Cells were treated with TPA at various times following preincubation with or without KB-R7785. Blotted samples were probed with antibodies against PLZF after immunoprecipitation with anti-HB-EGF-CTF antibody (upper panel). The total amount of HB-EGF-CTF in the immunoprecipitates was determined by reprobing the same blot with an anti-HB-EGF antibody (lower panel).