Figure 1. Nuclear-encoded factors acting within mitochondria.
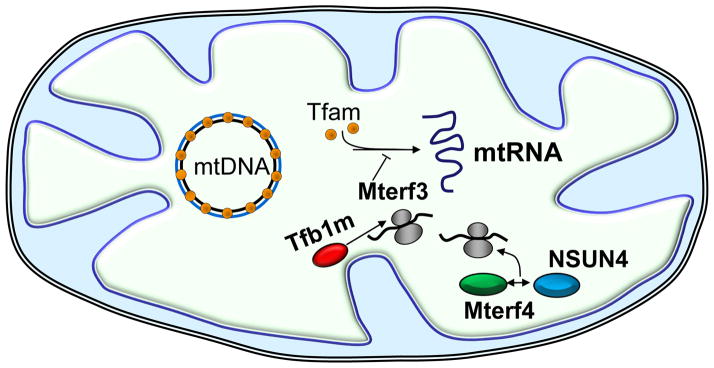
Targeted gene disruptions in mice (knockouts) have helped define the functions of several nuclear genes encoding products that function within mitochondria (as described in the text) including: Tfam (orange spheres), binds the mtDNA at multiple sites and functions in both mtDNA maintenance and transcription initiation; Mterf3, functions as a negative regulator of mtDNA transcription; Tfb1m (red ellipse) and Mterf4 (green ellipse), participate in mitochondrial ribosome assembly. Tfb1m is a dimethyltransferase that catalyzes the adenine dimethylation of the small ribosomal RNA required for ribosome assembly and translation. Similarly, a complex containing Mterf4 and the rRNA methyltransferase, NSUN4 (blue ellipse), participates in the assembly of the large ribosomal subunit.
