Figure 3. Proposed integration of energy-generating and antioxidant pathways by PGC-1α.
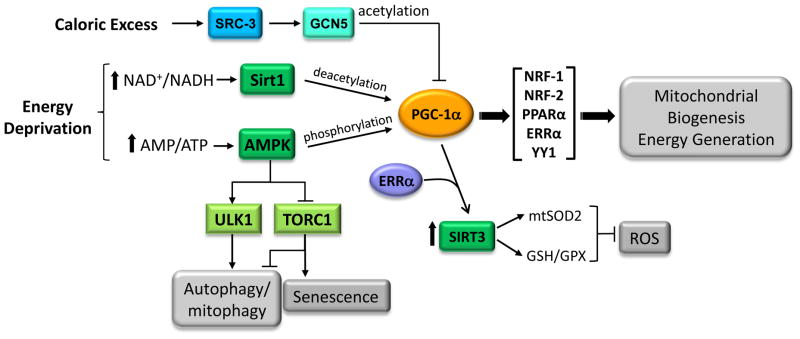
PGC-1α is activated via post-transcriptional phosphorylation by AMPK or by deacetylation via SIRT1 in response to nutrient deprivation. Induction or activation of the coactivator can enhance mitochondrial biogenesis and oxidative function through the coactivation of multiple transcription factors involved in respiratory gene expression (see Figure 2). PGC-1α activation may also promote an antioxidant environment by coactivating ERRα to induce SIRT3, a mitochondrial sirtuin that has been implicated in ROS detoxification. In addition, AMPK promotes autophagy through direct phosphorylation of ULK1 or suppression of the TORC1 kinase complex. Inhibition of the TORC1 pathway also has been shown to have a negative effect on senescence. Increased autophagy, enhanced ROS detoxification and inhibition of TORC1 are all associated with health and longevity. Under conditions of caloric excess, SRC-3 induces GCN5 which inactivates PGC-1α through acetylation.
