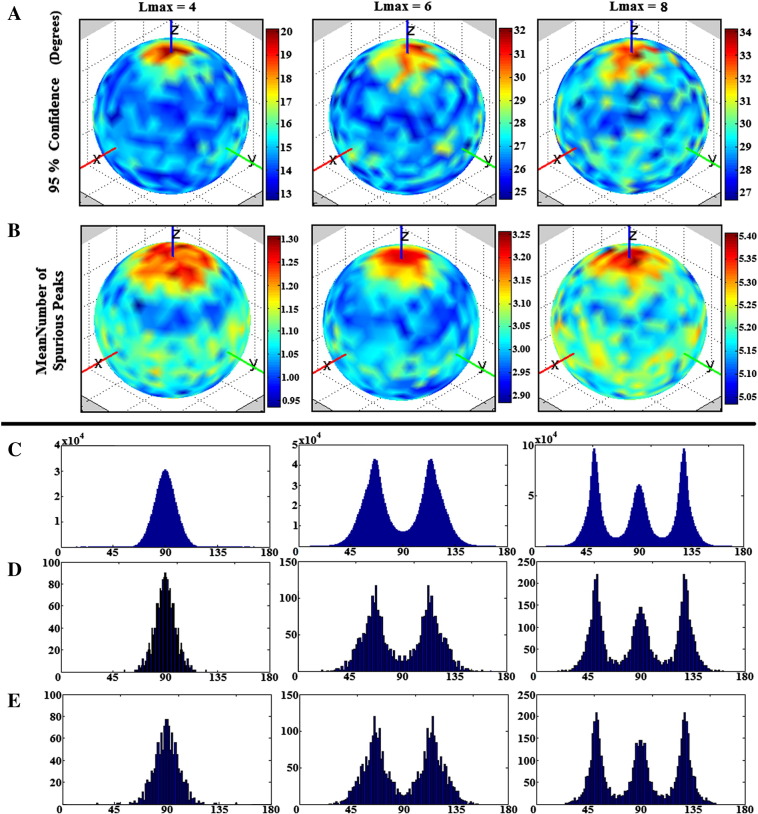
Fig. 9.
Impact of varying fibre orientation (simulation (iii)). (A) Plot of 95% confidence intervals for primary peak orientation (degrees). Note that there appears to be a pattern of increased uncertainty at along the Z axis which holds across the Lmax range. (B) A plot of the mean number of spurious peaks, note the correlation between A and B. (C) An aggregate distribution of all spurious fibre orientations relative to their primary peak. Notice that the distinct Lmax dependent banding appears to match axially-aligned results (D) Distribution of spurious peaks selected from a single fibre orientation chosen for its ‘typical’ 95% confidence interval and mean spurious peak count. (E) Distribution of spurious peaks selected from a single fibre orientation chosen for its a-typical 95% confidence interval and mean spurious peak count. Notice the distinct similarity between plots D and E.