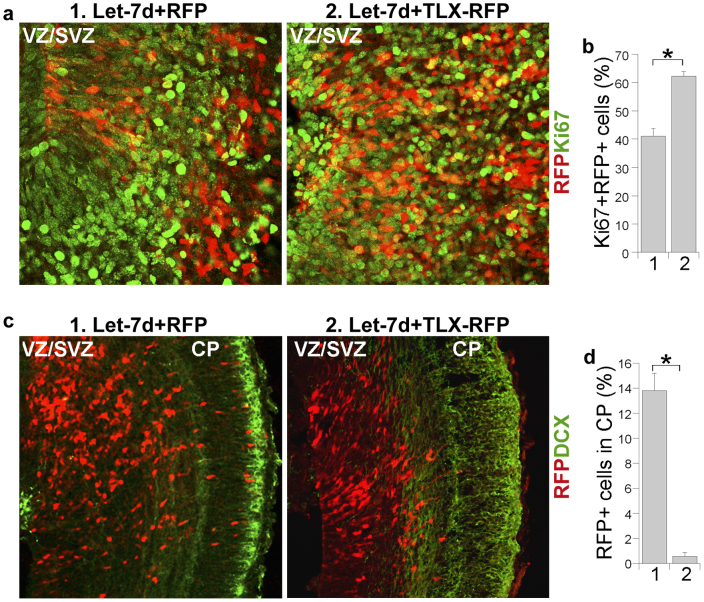
Figure 5. Suppression of TLX expression is critical for let-7d function in inhibition of neural stem cell proliferation and promotion of neuronal differentiation and migration.
(a). Co-expression of TLX lacking its 3′ UTR with let-7d (let-7d + TLX-RFP) restored let-7d-reduced levels of cell proliferation in the germinal zone of embryonic mouse brains. VZ/SVZ stands for ventricular zone and subventricular zone. The transfected cells were RFP+, shown in red. The proliferating cells were Ki67+, shown in green. (b). Percentage of the Ki67+RFP+ cells over total RFP+ cells in let-7d + RFP-transfected brains (1) and let-7d + TLX-RFP-transfected brains (2). Error bars are standard deviation of the mean. * p<0.05 by Student′s t-test. (c). Co-expression of TLX lacking its 3′ UTR reversed let-7d-induced premature cell migration to the cortical plate. The transfected cells were RFP+, shown in red. DCX staining (green) was included to show the brain structure. CP stands for cortical plate. (d). Quantification of transfected cells (RFP+) that migrated to the CP in let-7d + RFP (1) and let-7d + TLX-RFP (2)- electroporated brains. *p<0.001 by Student's t-test. Error bars are standard deviation of the mean for both panels (b) and (d).