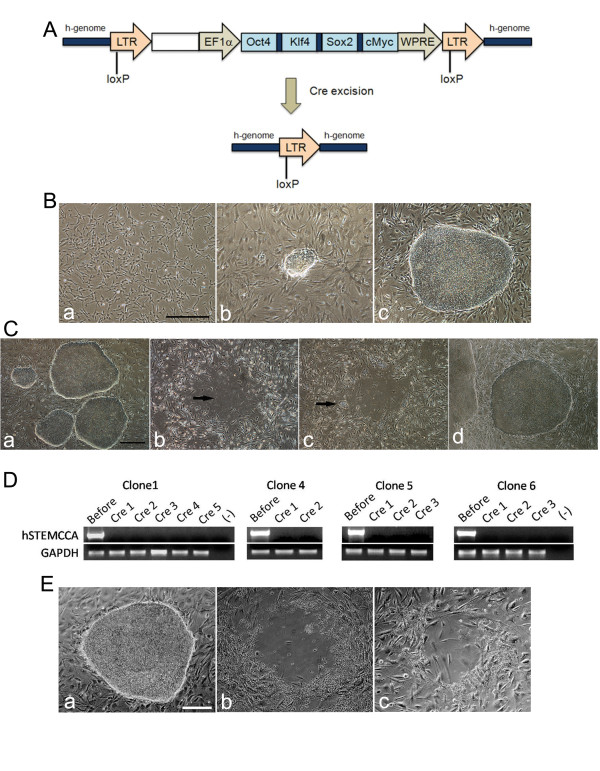
Figure 1.
Generation of transgene-free SCAP iPSCs. (A) Schematic representation of the hSTEMCCA-loxP lentiviral vector integrated into the human cell genome (h-genome) after transduction of SCAP. A loxP site was introduced within the U3 region of the 3' LTR. Following the exposure of pHAGE2-Cre-IRES-PuroR plasmid, the entire cassette was excised. (B) Emergence of SCAP iPSCs during reprogramming. (B-a) SCAP at passage (p) 0 before transduction. (B-b) SCAP at p3 were transduced with hSTEMCCA-loxP lentiviral vector and seeded onto MEF. A small ESC-like colony emerged on day nine post transduction. (B-c) A SCAP ESC-like colony on day 28 post transduction on MEFs. The ESC-like colony is considered at p0. (scale bar: 500 μm). (C) Excision of hSTEMCCA. (C-a) Established SCAP iPSC colonies at p2 before transgene excision. (C-b) After pHAGE2-Cre-IRES-PuroR plasmid transfection and 48 hours of pluromycin treatment, most SCAP iPSC colonies died out leaving behind an empty space (arrow). (C-c) New colonies (arrow) emerged on day 1 after Cre-excision and puromycin selection. (C-d) Expanded SCAP iPSC colonies passaged twice after Cre-excision. (scale bar: 500 μm). (D) Excision of hSTEMCCA was verified by RT-PCR. Clones after cre-excision showed no detectable hSTEMCCA. GAPDH served as a control. (E) A clone of TF-SCAP iPSCs grown on DR4 MEFs was treated with puromycin (1.2 μg/mL) for up to a week. (Ea) Before the addition of puromycin. (Eb) On day 2 after the addition of puromycin. (Ec) On day 4 after puromycin treatment. (scale bar: 250 μm). ESC, embryonic stem cells; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblasts; SCAP, stem cells from apical papilla.