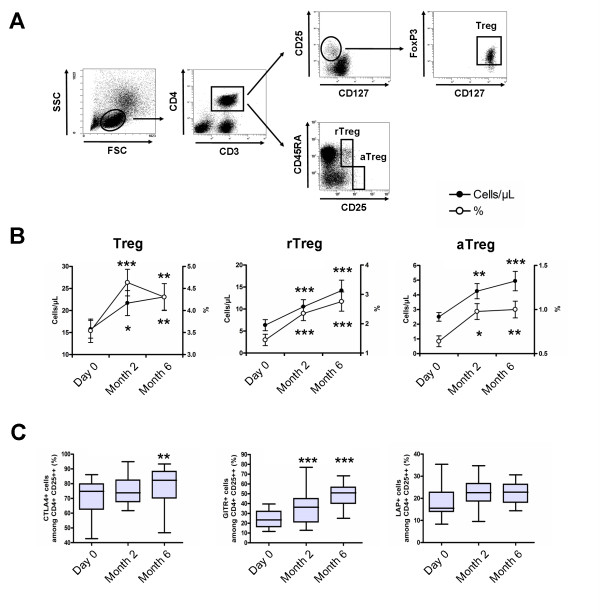
Figure 4.
Vitamin D supplementation induces a significant increase of regulatory T cells. (A) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in the lymphocyte light-scatter gate were analyzed for CD3, CD4, CD25, CD127, CD45RA and FoxP3 staining. Regulatory T cells (Tregs), resting Tregs (rTregs) and activated memory Tregs (aTregs) were defined as CD3+CD4+CD25hiCD127-FoxP3+ cells, CD3+CD4+CD25++CD45RA+ cells and CD3+CD4+CD25+++CD45RA- cells, respectively. (B) Time evolution of peripheral blood Tregs, rTregs and aTregs in percentage and absolute number. (C) Time evolution of CTLA4, GITR and LAP expression by Tregs. Peripheral blood Tregs, rTregs and aTregs increased under vitamin D supplementation, as did the expression of molecules associated with suppression of Tregs. Mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) is shown in panel B. Box plots in panel C indicate median, interquartile ranges, minimum and maximum values. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus Day 0; Wilcoxon test.