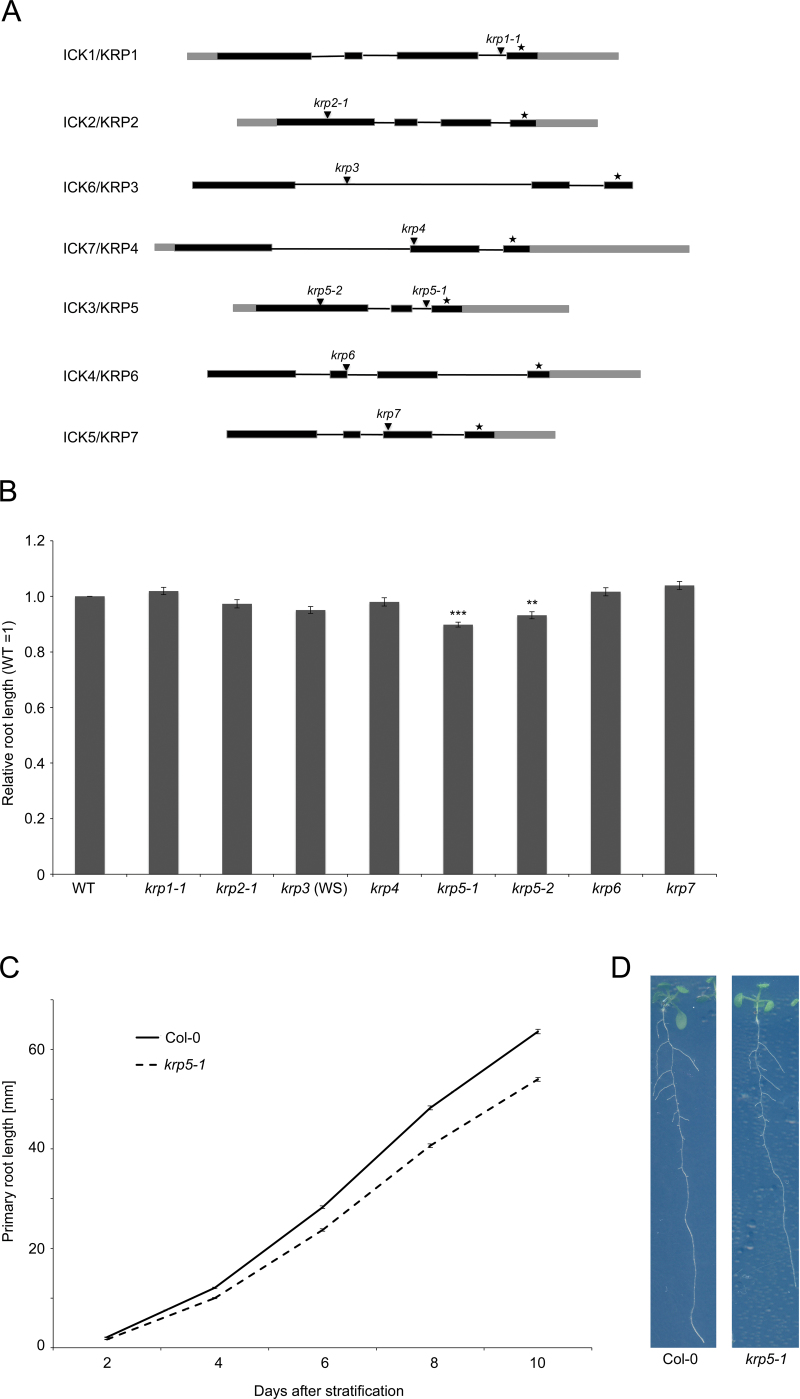
Fig. 1.
ICK/KRP gene family structure, mutants, and primary root phenotypes. (A) Gene structure of the seven members of the ICK/KRP family. Black boxes and lines indicate predicted exons and introns, respectively, grey boxes indicate untranslated regions, asterisks indicate the most conserved exon, which includes the CDKA and CYCD binding sites, and arrowheads indicate the positions of T-DNA insertions in the loss-of-function mutants used in this study. (B) Primary root length of the ick/krp loss-of-function mutants relative to WT. Seedlings were grown vertically for 10 days and root lengths are relative to Col-0 for all mutants except krp3 which was relative to WS. *** indicates t-test P < 0.001; ** indicates P < 0.05 (n = 40). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. (C) Average primary root lengths of WT and krp5-1 plants at 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 days after completion of stratification. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (n = 40). (D) Representative examples of 10-day-old Col-0 and krp5-1 seedlings showing a reduction of primary root growth in krp5-1 (this figure is available in colour at JXB online).