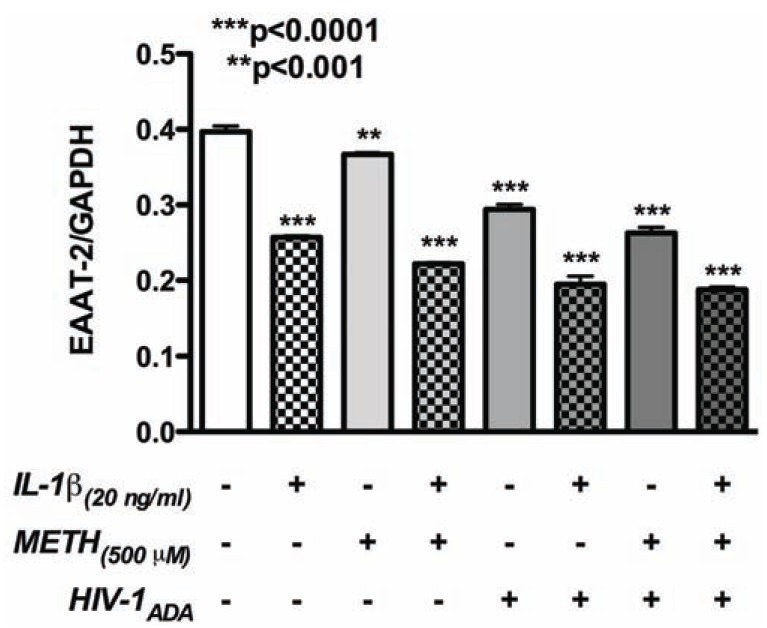
Fig. (2).
METH, HIV-1, and inflammatory mediators alter EAAT-2 mRNA expression. Primary human astrocytes were treated with METH (500 µM), HIV-1ADA, and IL-1β (20 ng/mL) for 24 hours. Real-time PCR was performed to determine the mRNA expression patterns of EAAT-2. METH, HIV-1ADA and IL-1β independently led to significant decreases in EAAT-2 mRNA levels. A combination of stimuli further attenuated EAAT-2 mRNA levels indicating additive/synergistic effects. Astrocyte RNA was extracted with Trizol reagent (Life Technologies Corp., Carlsbad, CA) and reverse-transcribed into cDNA as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Life Technologies). TaqMan® 5' nuclease gene expression assays for EAAT-2 (Life Technologies, C/N: hs00997364_m1) and glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH; C/N: 4310859) were performed using a StepOnePlus system (Life Technologies). The reactions were carried out at 48°C for 30 min, 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 s and 60°C for 1 min. Gene expression was expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) of triplicates and are representative of 3 astrocyte donors tested as biological replicates. Multiple additional astrocyte donors were examined in smaller subsets of treatment conditions in several other experiments. In each experiment, individual conditions were tested with a minimum of triplicates. Gene expression was compared by one-way analysis of variance followed by Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons post-tests (Prism 5.0, GraphPad software, La Jolla, CA, USA).